Business Model Design Guide
What is Business Model Design?
In this guide we will focus on defining your business model, the business model specifies the way your company will generate revenue and make a profit.
For this, we will be using the business model canvas, a framework developed by strategyzer.
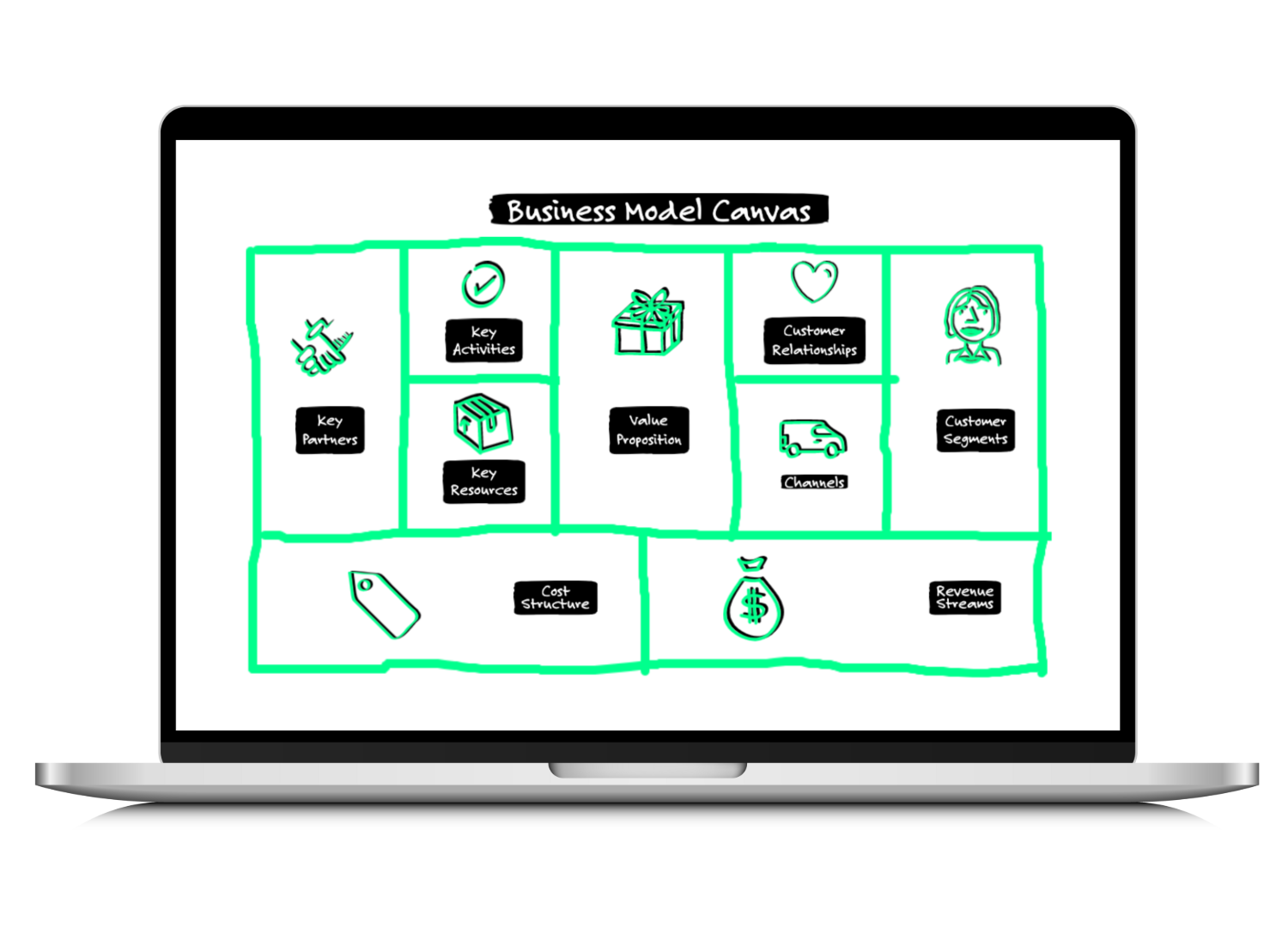
The business model canvas is a visual tool used to describe and understand the different elements of a business model. It will help you to visualize and plan out the different components in a structured and logical way and understand how they fit together.
The canvas consists of nine building blocks that represent the key elements of a business model. So throughout the day, you will dive into and work on each of those building blocks.
- Value proposition: This describes the unique value that your company’s products or services offer to customers.
- Customer segments: This identifies the specific groups of customers that your company is targeting.
- Channels: This describes the ways in which your company will reach and communicate with its customers, such as through its website, retail stores, or other channels.
- Customer relationships: This describes the nature of the relationships and how your company interacts with its customers, as well as how those interactions might vary for different types of target customers.
- Key activities: This identifies the key activities that your company needs to perform in order to create and deliver its products or services, such as research and development, manufacturing, or marketing.
- Key resources: This identifies the resources that your company needs to create and deliver its products or services, such as people, technology, or physical assets.
- Key partners: This identifies the key partners that your company works with, such as suppliers, distributors, or other companies.
- Revenue streams: This identifies the ways in which your company generates revenue, such as through the sale of products, subscriptions, or fees.
- Cost Structure: This identifies the key expenses that your company incurs in order to create and deliver its products or services, such as salaries, rent, and other costs.
Note: 🍋 Throughout this guide, we will use the example of a food supplement company to better illustrate each task and information.
What is Business Model Design Good For?
Defining a robust business model is crucial as it serves as a roadmap that guides decisions, resource allocation, and strategic planning. A well-defined business model not only helps you understand how your company will make money but also provides clarity on essential aspects such as target customers, value proposition, and key activities. By taking the time to outline your business model, you will be able to:
- Gain Clarity and Alignment: The Business Model Canvas enables you to clearly articulate and understand key business components in a visual format, fostering a shared understanding regarding value creation.
- Obtain a Holistic View: Breaking down the business into nine essential blocks, the canvas provides a holistic view, facilitating examination of interdependencies among the different elements.
- Work through an Iterative Process: As a dynamic tool, the canvas supports easy modification, crucial for startups iterating on their business model based on evolving insights into customers, market dynamics, and competition.
- Identify Potential Risk and Challenges: The Business Model Canvas helps founders map out the entire business model, allowing them to identify potential risks and uncertainties. This proactive approach enables the development of strategies to mitigate risks and better prepares you for challenges.
- Maintain a Customer-Centric Approach: Focused on customer segments, value propositions, and relationships, the Business Model Canvas encourages a customer-centric approach. It aids you in understanding customer needs and aligning the business model accordingly.
Curated Lists 📋
💡 To save you some time, we have prepared a free Sales Channel Glossary and a free Markeitng Channel Glossary with which you can use for your Business Model Design.
How to Design Your Business Model Step-by-Step:
Step A: Business Model Template
Step B: Value Proposition
Step C: Customer Segments
Step D: Sales & Marketing Channels
Step E: Customer Relationships
Step F: Key Activities
Step G: Key Resources
Step H: Key Partners
Step I: Revenue Streams
Step J: Cost Structure
Step A
Business Model Template
To work on your business model you can either build your own whiteboard template for example on Miro or you can use our ready-to-use template along with this guide.
Included Templates:

Business Model Design Miro Board

Step B
Value Proposition

At this point you should have defined your Value Proposition, however if you didn’t and want to go more into detail you can use the specific toolkit on value proposition design which you will also find in our basecamp library.
But if you prefer, you can also just use the quick and dirty approach to define your value proposition as a part of your business model:
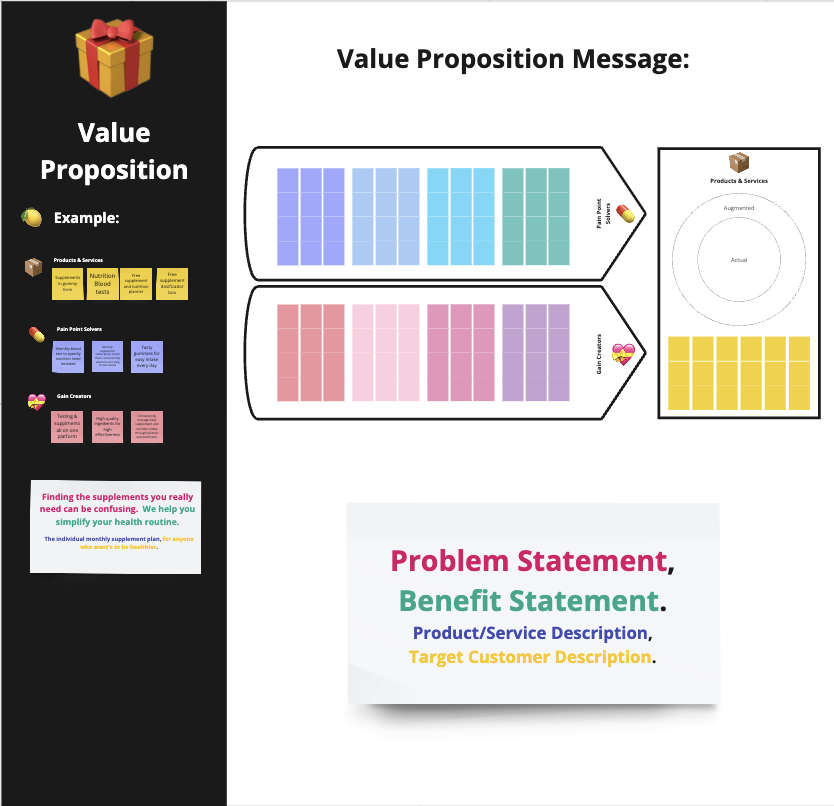
Your value proposition essentially can be explained through the following 3 aspects:
- Product/Service Features: These are the specific attributes and functionalities of your offering that set it apart from competitors and provide tangible benefits to your customers.
- Pain Point Solvers: These address the problems, challenges, or needs your customers have, offering solutions that alleviate their pain points and improve their lives.
- Gain Creators: These represent the unique advantages and benefits your product or service brings to customers, going beyond addressing pain points to create positive outcomes and value for them.
Go ahead, define each of those elements and note them down on your business model 📒 template.
Bearing those elements in mind, you can now define your value proposition message, describing it in one sentence. Imagine for example you want to define the header message for your website or landing page, what would you say to explain your value proposition in 2 lines and catch the attention of your visitors.
To define your value proposition, we will use a four parts approach. Your message should contain 4 types of information:
-
Problem Statement: What is the problem you are solving with your product/service?
-
Benefit: What benefit does your product/service offer that solves this problem?
-
Product/service category: What is it that you are offering? Which term does describe your product/service?
-
Target Customers: To whom are you offering this product/service?
So go to your business model 📒Template and formulate your value proposition using this structure.
Step C
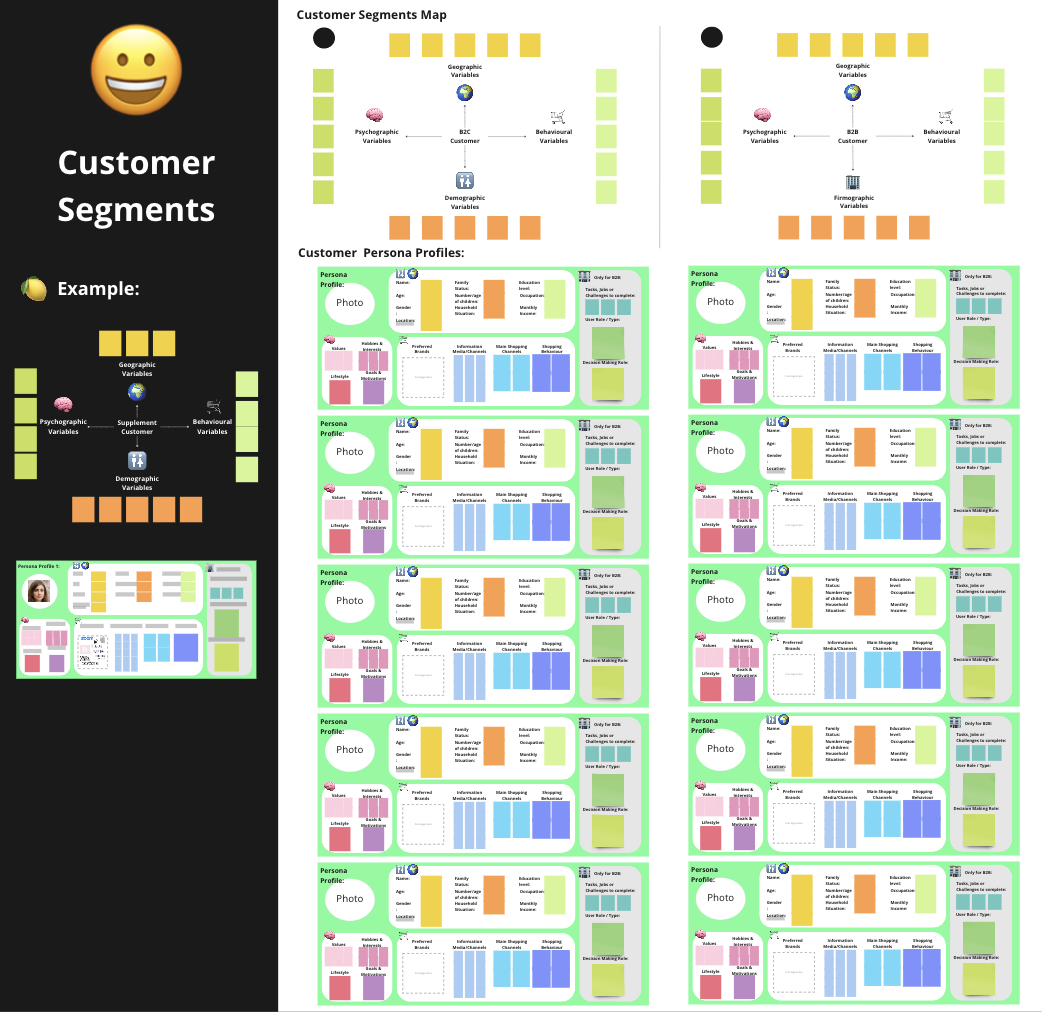
Customer Segments

Your target customer segments are another building block that you should already have defined at this stage. If you didn’t and want to work through your customer segments in a detailed way, you can find the corresponding exercises in the customer deep dive toolkit.
In any case, you should have done some kind of market research and consumer analysis before hopping into the ideation and design process. So with this information in mind, use the customer segmentation and customer persona model on your business model template to clearly outline who your target customers are.
Customer segmentation: Define your target customer segments using the customer segmentation map A if you’re targeting B2C clients and B if you’re targeting B2B clients. Describe your target segments using:
-
-
Demographic/firmographic variables: These variables include age, gender, income, education, and family size. They help categorize individuals based on their personal characteristics. For B2B, this includes business-specific characteristics such as industry, company size, revenue, and location.
-
Geographic variables: These variables consider the physical location of your customers, such as country, region, city, or climate zone.
-
Psychographic variables: Psychographic factors relate to lifestyle, values, interests, and personality. These help understand customers’ behaviors and motivations.
-
Behavioral variables: Behavioral variables consider how customers interact with products or services, including usage patterns, brand loyalty, or purchase frequency.
-
Customer Personas: Define a customer persona for each of the segments you’re targeting by using the customer persona profiles. Imagine who your potential persona is and fill in all the variables.
Step D
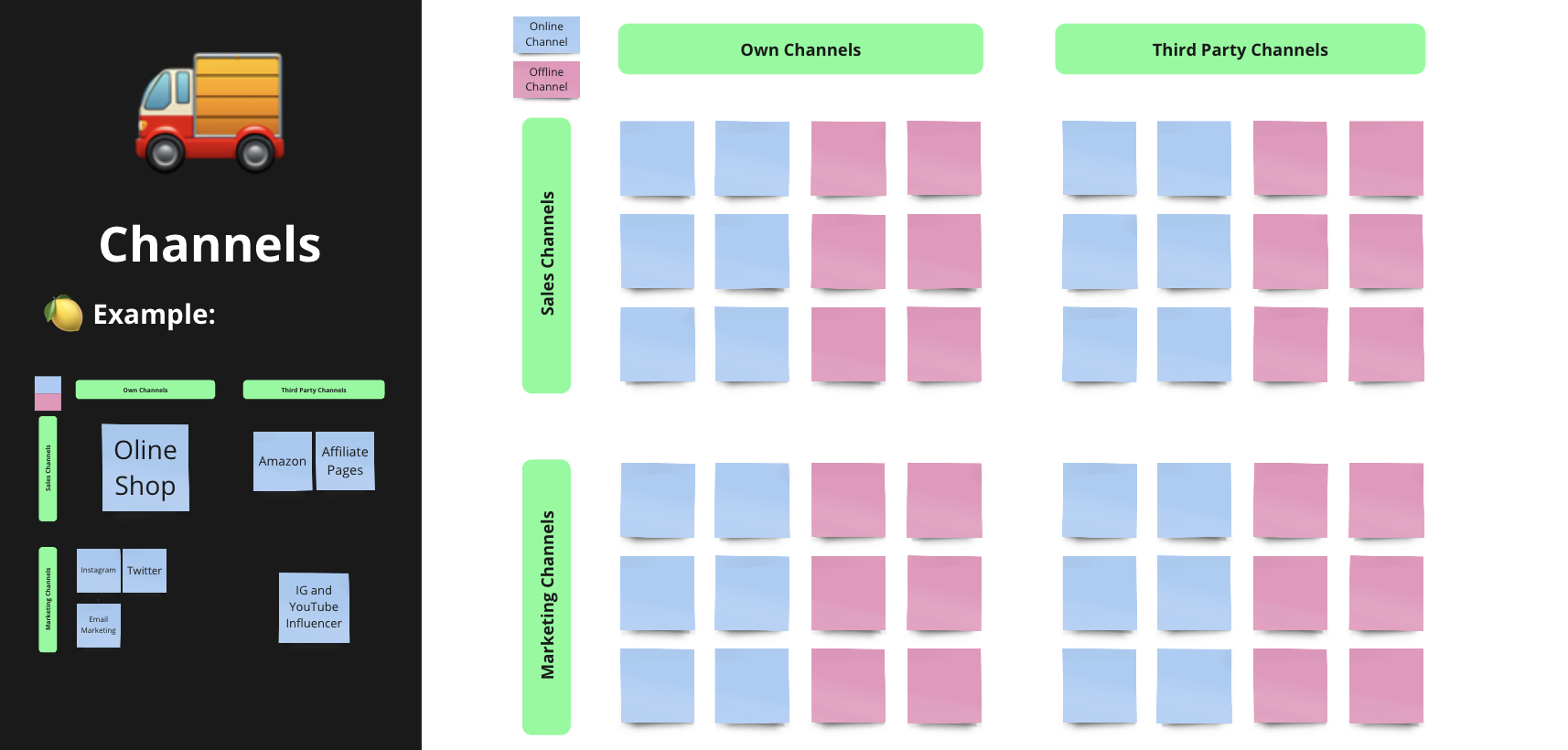
Sales & Marketing Channels

Within this block of your business model canvas, you need to identify the ways in which you will interact with your customer segments. There are different types of channels we can differentiate.
On the one hand, there are:
- Sales channels: The various ways in which a business can sell its products or services to customers.
- Marketing channels: The various ways in which a business can reach and communicate with its target customers. Marketing channels are used to promote products or services and build brand awareness, but do not necessarily involve a direct sale.
These may include both
- Direct or owned channels: Channels that involve a direct interaction between the business and the customer and that are usually owned by the company itself.
- Indirect or paid channels: Channels that involve intermediaries between the business and the customer.
And those again might be digital channels that work online or traditional channels that work offline.
💡 You can use the Sales Channel Glossary List above to identify your sales channels.
💡 You can use the Market Channel Glossary List above to identify your marketing channels.
When defining your channels, you want to:
- Consider what you want to achieve through your channels, such as increasing brand awareness, generating leads, or making sales.
- Look into the various channels that are available to you and consider which ones are most likely to help you achieve your goals.
- Consider which channels are most likely to be effective in reaching and engaging your customer segments. This may depend on factors such as the preferences and behaviors of your customers, as well as the unique characteristics of each channel.
- Think about the resources you have available to invest in your channels, such as time, money, and personnel. This will help you prioritize which channels to focus on.
☝️ Use the corresponding area of your Business Model 📒Template to specify the channels you will be using.
Step E
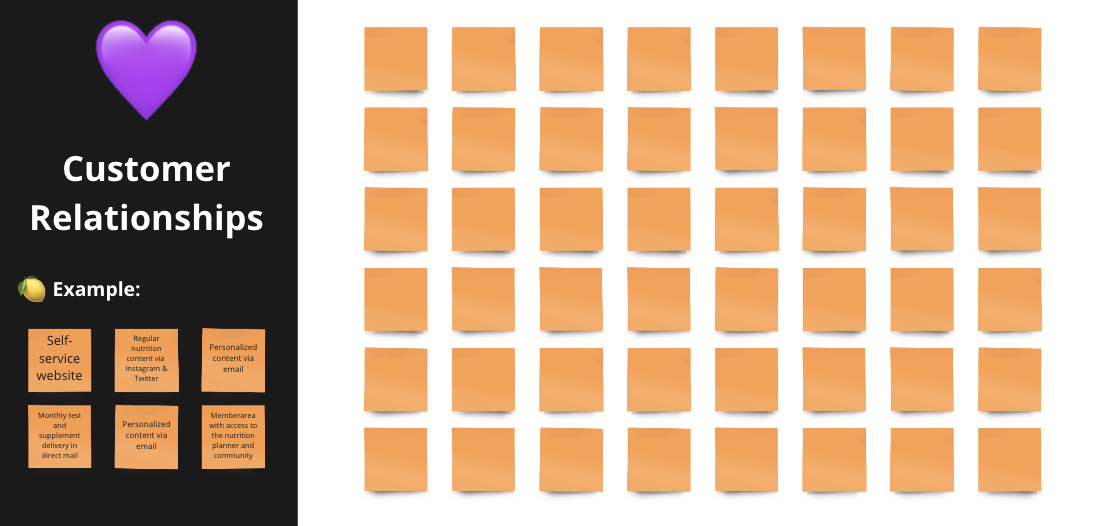
Customer Relationships

The customer relationships block is an important part of your business model because it helps you to understand how your company interacts with its customers , how it builds, nurtures and maintains those relationships and how it can create value for them. By understanding the different types of customer relationships, you can identify the most effective ways to engage with your customers and build long-term loyalty. Depending on the target segment your way of interacting with a customer can differ, for example while Baby Boomers probably prefer personal assistance, Millennials rather go online to research and purchase products on their own.
Try to identify the potential ways you would be interacting with your different customer segments in different touchpoints.
Ways of interacting with your customers can be, for example:
- Personal assistance: Providing one-on-one support and guidance to customers through channels such as phone, email, or in-person meetings. Personal assistance can help build strong relationships with customers and improve the overall customer experience.
- Self-service: Allowing customers to find answers and solve problems on their own through resources such as online FAQs or knowledge bases. Self-service can be convenient for customers and can help reduce the workload of customer service teams.
- Automated services: Using technology such as chatbots or automated emails to interact with customers and provide support. Automated services can be a cost-effective way to provide support, but can also be less personalized than other forms of customer interaction.
- Communities: Building online or offline communities where customers can connect with each other and share experiences and advice. Communities can help build a sense of belonging and loyalty among customers, and can also be a source of valuable feedback and ideas for the business.
- Co-creation: Involving customers in the design and development of products or services, through techniques such as crowdsourcing or co-creation workshops. Co-creation can help build strong relationships with customers and create products or services that are tailored to their needs and preferences.
- Personalized communication: Sending targeted and personalized communication to customers based on their preferences and behavior, such as through email marketing or targeted ads. Personalized communication can help build a sense of connection with customers and improve the effectiveness of marketing efforts.
- Customer feedback: Gathering feedback from customers through methods such as surveys, reviews, or social media comments. Customer feedback can help businesses understand what is working well and what requires improvement, and can help inform decisions about products, services, and overall customer experience.
- Customer support: Providing assistance to customers who require help with using a product, understanding a service, or resolving an issue. Customer support can help build trust and loyalty with customers, and can also be a source of valuable insights for the business.
- Promotions & contests: Offering promotions or contests to customers as a way to drive sales and engagement. Promotions and contests can be a fun and effective way to build relationships with customers.
- Content: Creating and sharing content such as blog posts, videos, or social media posts that educate, entertain, or engage customers. Content can be a powerful way to build relationships with customers, and can also help drive traffic and sales to the business.
- Events: Hosting events such as workshops, seminars, or trade shows where customers can interact with the business and each other in person. Events can be a great way to build relationships with customers and create a more immersive and interactive experience. Events can also be a valuable marketing and networking opportunity for the business.
There are of course many more ways in which you could interact with your customers.
☝️ Go ahead and think about which ones would be the most relevant for your target customers and note them down in the respective area on your Business Model 📒Template.
Step F
Key Activities

Next, let’s take a look at the key activities within your business model. Key activities refer to the most crucial tasks that a business must perform in order to generate and deliver value to its customers. These activities can be related to production, marketing, distribution, customer service, or any other core aspect of the business.
Key activities play a vital role in the business model canvas, as they aid in comprehending what the business must do to create and capture value for its customers. By recognizing and prioritizing key activities, the business can concentrate its resources and efforts on the most significant aspects of its operations.
First, it is important to identify all the vital activities in the value generation process. Then, prioritize them by considering which activities are most critical to the business and which are less significant. These key activities should be the centerpiece of the business model and the focus of its resources and efforts.
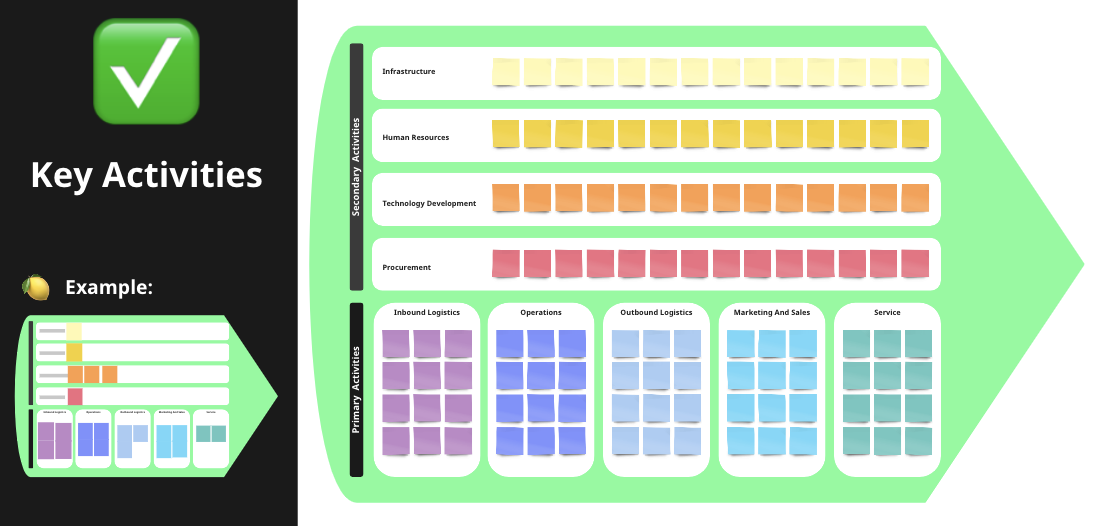
A useful framework for identifying key activities is the value chain model developed by Michael Porter. This model helps understand the various tasks businesses go through in designing, producing, marketing, delivering, and supporting their products or services.
The value chain model separates business activities into two categories: primary activities and support activities. Primary activities are directly involved in creating and delivering a product or service, such as inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing and sales, and service. Support activities provide indirect support to the primary activities, such as procurement, human resource management, and technology development.
By comprehending the activities involved in delivering value to customers, businesses can identify ways to attain a competitive advantage and improve efficiency and effectiveness. The value chain model, in conjunction with the business model canvas, can assist businesses in understanding how to create and capture value for their customers.
The value chain model identifies the following primary activities:
- Inbound: Activities related to obtaining and managing the inputs necessary for the business to operate.
- Operations: Activities related to creating the goods or services, such as manufacturing, assembly, programming or service delivery.
- Outbound: Activities related to delivering the final product or service to the end-users and providing access to the product or service.
- Marketing and sales: Activities related to promoting and selling products or services to customers.
- Service: Activities related to providing after-sales support, such as repairs, maintenance, and customer service.
The value chain model also identifies the following support activities:
- Procurement: Activities related to purchasing goods and services needed for the business.
- Human resource management: Activities related to recruiting, hiring, training, and managing employees.
- Technology development: Activities related to developing and maintaining the technological infrastructure of the business, such as research and development, design, and testing.
- Infrastructure: Activities related to managing the overall operations of the business, such as finance, legal, and administration.
☝️ So go ahead and look at each block of this framework starting with the primary activities. Use your Business Model 📒Template and note down the key activities you will have to complete within each category on the post-its.
Step G
Key Resources

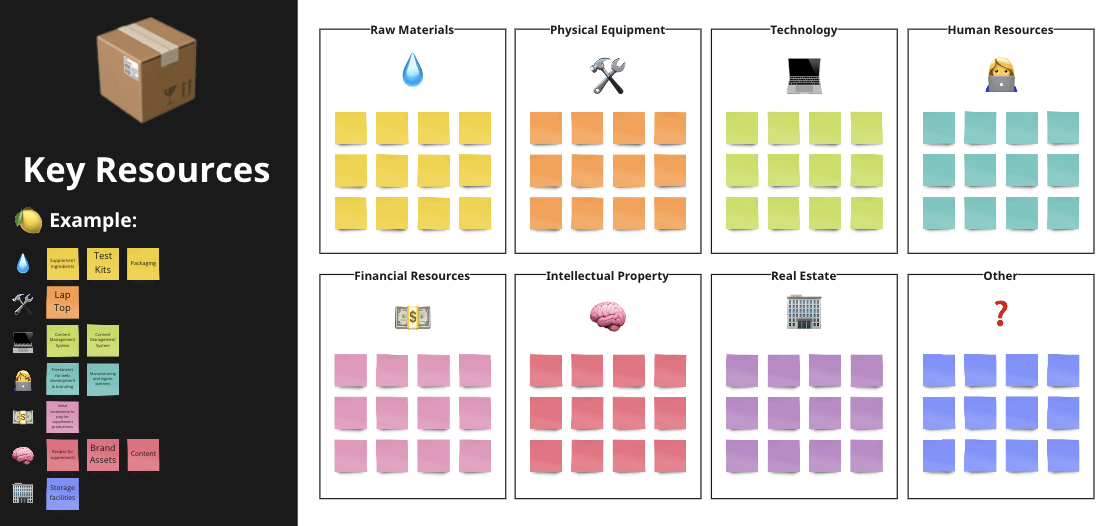
Another important element of your business model are your “key resources”. Key resources refer to the resources that your business needs in order to create and deliver value to your customers. These can be physical, such as raw materials, equipment, or real estate; human, such as employees or expertise; financial, such as capital or credit; or intangible, such as intellectual property or brand reputation. By understanding your key resources, you can ensure that you will have access to the resources you need to operate your business effectively and efficiently.
Types of resources can include:
- Raw materials: Raw materials are resources that are used as inputs in the production of goods or services, such as metal, wood, or oil.
- Physical equipment: Physical equipment refers to tools, machinery, and other physical assets that are used in the production, marketing, or delivery of goods or services. This can include everything from manufacturing machines and office equipment to vehicles and real estate.
- Technology: Technology refers to systems, tools, and platforms that enable businesses to create and deliver value to customers in new and innovative ways, and to improve efficiency and competitiveness. This can include everything from production technology and marketing technology to customer service technology and data analytics technology.
- Human resources: Human resources refer to the employees and expertise that are necessary for the operations of a business. This can include everything from skilled labor and management to research and development and customer service.
- Financial resources: Financial resources refer to capital and credit that are necessary to fund the operations and growth of a business. This can include everything from cash and investments to loans and lines of credit.
- Intellectual property: Intellectual property refers to patents, trademarks, and other forms of intellectual property that protect and differentiate a business’s products or services. This can include everything from patents on new technologies to trademarks on brand names and logos.
- Real estate: Real estate refers to land, buildings, and other physical assets that are necessary for the operations of a business. This can include everything from retail stores and warehouses to office buildings and manufacturing facilities.
☝️ Go through every of those categories and think about which resources you are going to be crucial to be able to deliver your value proposition to your customers. Note them down in the respective area of your Business Model 📒Template.
Step H
Key Partners

The seventh block, ‘Key Partners,’ refers to the strategic alliances, partnerships, and networks that your business relies on to create and deliver value to its customers. These partners can provide access to resources, expertise, markets, or distribution channels that are necessary for the business to operate effectively and efficiently.
Key partners can include suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, marketing and sales partners, and other businesses that play a critical role in the value creation process. It is important to identify key partners as they can help your business access resources and expertise that it may not have in-house, as well as expand its reach and scale operations.
Examples of key partners include:
- Suppliers: businesses that provide raw materials, components, or other goods and services necessary for the business’s operations.
- Manufacturers: businesses that produce goods or components on behalf of another business.
- Distributors: businesses that handle the distribution of goods or services to customers.
- Marketing and sales partners: businesses that help a business promote and sell its products or services to customers.
- Research and development partners: businesses or organizations that collaborate with a business on research and development projects.
- Service providers: businesses that provide support services, such as legal, finance, or IT, to a business.
☝️ Go ahead and consider the different partners in these areas that you will need to work with to deliver your value proposition. Note them down on post-its in the corresponding area of your Business Model 📒Template.

Step I
Revenue Streams

Next you want to clearly define what your revenue streams are, meaning the sources of income that a business generates from its products or services, the ways in which a business captures value from its customers.
It is essential to clearly identify how your business will generate revenue and make money and which revenue streams are most appropriate and sustainable for a business to allocate resources accordingly.
There are different types of revenue streams and the appropriate revenue streams will depend on the nature of your business and its value proposition. Your business may have multiple revenue streams. It can actually be quite beneficial to diversify revenue streams in order to reduce risk and improve the sustainability of a business.
Common types of revenue streams are for example:
Sales Revenue:
- Product Sales: Revenue generated from selling physical goods or products.
- Service Sales: Revenue from providing services to clients or customers.
Subscription Revenue:
- Subscription Services: Regular revenue from subscription-based models for access to products, services, or content (e.g., software as a service – SaaS, streaming services).
- Membership Fees: Recurring revenue from individuals or organizations for access to exclusive benefits, services, or resources.
Advertising Revenue:
- Display Ads: Revenue generated from displaying third-party advertisements on websites, apps, or other platforms.
- Sponsored Content: Earning revenue by featuring sponsored content or partnerships within owned media channels.
Rental or Usage Fees:
- Rental Services: Revenue from renting out physical assets or properties (e.g., real estate, equipment).
- Pay-per-Use: Charging customers based on usage or consumption (e.g., pay-per-view, pay-as-you-go services).
Licensing or Royalties:
- Licensing Fees: Revenue from licensing intellectual property (IP), patents, trademarks, or copyrights to third parties.
- Royalties: Earnings based on the use or sale of licensed IP, typically for books, music, or software.
Affiliate Revenue:
- Affiliate Marketing: Earning commissions by promoting or selling third-party products or services through affiliate links or partnerships.
Freemium or Premium Upgrades:
- Freemium Models: Offering basic services or products for free and charging for premium features or enhanced versions.
- Premium Add-ons: Charging for additional features, extensions, or upgrades to a basic product or service.
Consulting or Professional Services:
- Consulting Fees: Revenue from providing advisory or consulting services to clients.
- Training & Workshops: Revenue generated from conducting training sessions, workshops, or educational programs.
Commissions or transaction revenues:
- Sales Commissions: Earnings from receiving a percentage of sales as commission (e.g., affiliate sales, real estate commissions).
- Transaction Revenues: Charging a fixed fee or percentage for each transaction.
- Brokerage Fees: Revenue from acting as an intermediary in transactions (e.g., financial brokerages, real estate brokerage).
Crowdfunding or Donations:
- Crowdfunding Campaigns: Collecting funds from individuals or groups to finance projects or products.
- Donations: Receiving contributions or donations for causes, charities, or non-profit organizations.
☝️ Think about all the potential ways your business would generate income and describe them and note them down in the corresponding area of your Business Model 📒Template.
Step J
Cost Structure

And finally, you want to take a look at the potential expenses that you can expect your business to incur in order to create and deliver its products or services and generate revenue and make a profit.
Identifying and understanding the cost structure of your business allows you to understand the costs associated with its operations and identify opportunities for cost savings or efficiency improvements. On the other hand, it’s important to consider your cost structure when developing pricing strategies to ensure that your business is generating sufficient revenue to cover its expenses and make a profit.
A business’s expenses can be classified as direct and indirect costs or variable and fixed costs:
Direct costs are costs that can be directly traced to a specific product or service, such as raw materials and labor, that are directly involved in the production of a specific product. Indirect costs are costs that cannot be directly traced to a specific product or service but are still necessary for the operation of a business, such as rent, utilities, and general office expenses.
Variable costs are costs that vary in relation to the quantity of goods or services produced, such as raw materials and labor used in production. Fixed costs are costs that do not vary with changes in the volume of goods or services produced, such as rent and salaries of administrative staff.
Consider which expenses your business will have to incur. The types of costs and specific cost structure will depend on the nature of your business operations and value proposition. Common types of costs include:
- Raw materials and supplies
- Labor
- Rent and utilities
- Marketing and advertising
- Research and development
- Legal and regulatory compliance
- Insurance
- Taxes
- Office expenses
- Professional services
- Depreciation
- Interest
- Travel
☝️ Note them down in the corresponding area of your Business Model 📒Template.

With this, you should now have a complete overview of your business model. You can use the business model canvas as a starting point to develop and refine your business strategy and communicate your business model to others.