Customer Experience Management Guide

What is Customer Experience Management?
Another lever, and probably the most basic one, to retain and grow your customers is the customer experience you provide. If customers have a positive experience with your brand and products/services they are likely to stay loyal or even become advocates of your brand.
This is why a proper customer experience management is so essential. Customer experience management (CEM) refers to the process of designing, implementing, and monitoring the interactions that customers have with your business or brand.
Besides initially designing products/services and a value proposition that is centered around your customers, considering their needs and preferences, you can keep on improving the customer experience through CEM.
CEM encompasses activities such as:
- Mapping your customer journey and personalizing the customer experience on an individual or segmented level.
- Predicting potential pain points and providing good customer service and support at the right moments.
- Continuously collecting customer feedback and improving the customer experience accordingly.
Overall, CEM helps you to build long term relationships with your clients, increase customer loyalty, which in the end results in increased revenues.
Note: 🍋 Throughout this guide we will use the example of a food supplement company to better illustrate each task and information.
What is Customer Experience Management Good For?
A well-defined Customer Experience Management strategy is crucial as it directly impacts customer satisfaction, loyalty, and ultimately, business success.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: By prioritizing customer needs and preferences and delivering personalized experiences, CEM ensures higher levels of customer satisfaction, leading to increased retention and positive brand perception.
- Improved Customer Loyalty: Through proactive engagement, efficient problem resolution, and consistent delivery of value, CEM fosters stronger emotional connections with customers, driving loyalty and advocacy.
- Competitive Advantage: Businesses that excel in customer experience management gain a competitive edge by differentiating themselves based on superior service, leading to increased market share and profitability.
- Enhanced Revenue Generation: By increasing customer loyalty and advocacy, CEM directly contributes to revenue growth through higher retention rates, increased customer lifetime value, and positive word-of-mouth referrals.
Curated Lists 📋
💡 To save you some time, we have put together a free Survey Question Glossary and a free list with Customer Research Tools which will come in hand when working on your customer experience management.
How to Implement Customer Experience Management Step-by-Step:
Step A: Customer Experience Management Template
Step B: Personalized Customer Experience
Step C: Provide Customer Service and Support
Step D: Collect Customer Feedback
Step E: Analysis and Experience Optimization
Step A
Customer Experience Management Templates
To work your customer experience management you can either build your own whiteboard template for example on Miro and use Google Sheets to track customer satisfaction or you can use our ready-to-use templates along with this guide.
Included Templates:

Customer Experience Management Miro Board
Customer Satisfaction Dashboard Spreadsheet
Step B
Personalized Customer Experience

One way of improving the customer experience is through tailoring its different components to a customer segment or even on individual customer level. To do so we will take a detailed look at the different elements of the whole customer experience.
This is where your customer segmentation comes in again, because you can now use your customer segments and clusters as well the segmentation criteria on individual customer level, to inform your personalization activities. A customer segment refers to a group of potential or existing customers who share similar characteristics, needs, behaviors, or preferences. If you didn’t define your customer segments and clusters yet we recommend strongly to do so. You will find a detailed step by step process on how to to this in the customer segmentation toolkit.
Let’s get back to personalizing the customer experience, there are various ways how you can do this:
Personalized Product Recommendation:
Using customer data to recommend products or services based on a customer’s previous purchases or consumption, browsing history, or demographic information.
Examples:
- Amazon uses personalized product recommendations on their website and in their email marketing campaigns to suggest products that customers may be interested in based on their purchase history and browsing behavior.
- Spotify recommends personalized playlists and songs based on a user’s listening history and preferences.
Personalized Communication:
Tailoring messaging to individual customers or customer segments, using information such as their name, location, or purchase history.
Examples:
- Netflix uses personalized messaging in their email campaigns to promote new shows or movies that are similar to what a customer has already watched.
- Dunkin’ Donuts uses personalized communication in their mobile app by addressing customers by name in their push notifications and email campaigns. They also use customer location data to send personalized offers and promotions to customers based on the nearest Dunkin’ Donuts location.
Personalized Content:
Tailoring the content presented to customers based on their preferences, behaviors, and characteristics. Personalized content can include website content, blog posts, social media content, emails, and more.
Examples:
- Sephora: Sephora uses personalized content on their website and mobile app to suggest beauty products based on a customer’s purchase history, preferences, and skin type. They also offer personalized tutorials and product recommendations based on a customer’s makeup style and skill level.
- Nike: Nike uses personalized content on their website and mobile app to suggest workout plans and training programs based on a customer’s fitness goals and activity level.
Personalized Pricing, Offers (incl. Discounts), and Promotions:
Offering personalized discounts, promotions, or loyalty rewards to customers based on their purchase history or preferences.
Examples:
-
- Uber: Uber uses personalized pricing to offer customers discounts or promotions based on their previous ride history and usage patterns. For example, Uber may offer a discount code to a customer who hasn’t used the app in a while, or offer a promotion for a customer who frequently uses the app during peak times.
- Starbucks offers personalized discounts and promotions to their loyalty program members based on their purchase history and frequency.
Omni Channel Experience:
This refers to the use of multiple channels to engage with customers and provide a seamless experience across all touchpoints. This can include online and offline channels such as email, social media, in-store interactions, and mobile apps. By utilizing a variety of channels, businesses can provide customers with multiple ways to interact and engage with their brand and offer a more convenient and personalized experience.
Examples:
- Nike: Nike offers a seamless omnichannel experience by allowing customers to shop online, in-store, or through the Nike mobile app. Customers can purchase products online and pick them up in-store, or use the app to locate and reserve products at a nearby Nike store.
- Starbucks: Starbucks provides an omnichannel experience by allowing customers to order and pay for their drinks through the Starbucks mobile app, in-store, or through their website. Customers can also earn and redeem rewards across all channels.
Personalized Support and Customer Service:
Offering personalized customer service experiences by training representatives to address customers by name, understand their needs, offer relevant solutions or even have a system in place to recognize potential customer problems early.
Examples:
- Apple offers personalized support and customer service through their Genius Bar, where customers can receive one-on-one help with their Apple products.
- Zappos offers personalized customer service through their customer service hotline and online chat, where representatives are trained to provide personalized assistance and recommendations.
Customized Products/Services or Features:
Offering customized products or services that are tailored to individual customer preferences.
Examples:
- Adidas offers customized sneakers that can be designed with unique colors and patterns to match a customer’s style preferences.
- A travel company could offer customized travel packages that are tailored to a customer’s interests and preferences, such as offering unique experiences or activities based on their travel history.
Personalized Packaging:
This involves creating personalized packaging for products, such as adding a customer’s name or a personalized message.
Example:
- Coca-Cola has created personalized packaging for their customers by printing individual names on their bottles and cans.
- A food supplement company could include a personalized thank you note and indications and tips on how to use the supplements when delivering their supplement via mail.
✅ So to define how you could personalize your customer experience go to the first area of your Customer Experience Management 📒Template.

Start by mapping your customer journey by describing the various touchpoints and interactions a customer has with a business over time. Use the white post-its on the template to map out the key interactions and touchpoints at each stage of the life cycle:
- Awareness: The stage where a potential customer first becomes aware of a product or service.
- Consideration: The stage where a potential customer evaluates different options and considers whether a particular product or service meets their needs.
- Purchase: The stage where a customer makes a transaction and buys the product or service.
- On-boarding: The stage where a customer is introduced to and begins using the product or service.
- Usage: The stage where a customer regularly uses the product or service to meet their needs.
- After-sales: The stage where a customer receives post-purchase support and follow-up from the company.
- Loyalty: The stage where a customer becomes a repeat customer and advocates for the product or service to others.
Next, think about which kind of personalizations you can add at the different touch points along the customer journey. Use the coloured post-it and icons of the corresponding type of personalization and describe the personalization you want to include. Then place them along the customer journey as shown in the example.

Step C
Provide Customer Service and Support

Another important part of the customer experience is how you provide customer service and support. This can have a crucial impact on how customers perceive your brand since a great customer support could even make up for a bad experience. Nobody’s perfect, and it is totally normal for any business to have to deal with negative customer experiences or answer doubts and questions from time to time. To fully avoid them is quite impossible but you can plan ahead, by trying to identify and predict common pain points and have a solution at hand for when times comes.
There are a number of ways in which you can provide customer support and service which vary in terms of the difficulty to implement and their operational cost:
During your best practice research you probably identified different types of loyalty model, however, here is a overview of common types:
|
Channel |
Description |
Implementation Effort |
Cost to Operate |
|
Email support |
Offer support to customers through email, allowing them to reach out with questions, concerns, or feedback. |
Low |
Low |
|
Phone support |
Provide phone support to our customers, allowing them to speak directly with a customer service representative. |
Medium |
Medium |
|
Chat support |
Customers can chat with a customer support representative in real-time through an online chat feature on the website or in-app. |
High |
Medium |
|
Self-service support |
Offer a knowledge base or FAQ section on the website to provide customers with answers to common questions or issues. |
Medium |
Low |
|
Social media/ Community support |
Provide support to customers via social media channels, such as Twitter or Facebook or online communities . |
Medium |
Low |
|
In-person support |
companies with physical stores or locations can offer in-person support from customer service representatives or in-store associates. |
High |
High |
|
Video support |
offer video support to customers through platforms like Zoom or Skype, allowing to troubleshoot issues in real-time and provide personalized assistance. |
High |
Medium |
|
Chatbot support |
Utilize chatbots to provide quick and efficient customer support. |
Medium |
Low |
|
WhatsApp/ Telegram support |
Offer support to our customers via WhatsApp, Telegram or other messaging services either directly through a service representative or through a chatbot. |
Medium |
Low |
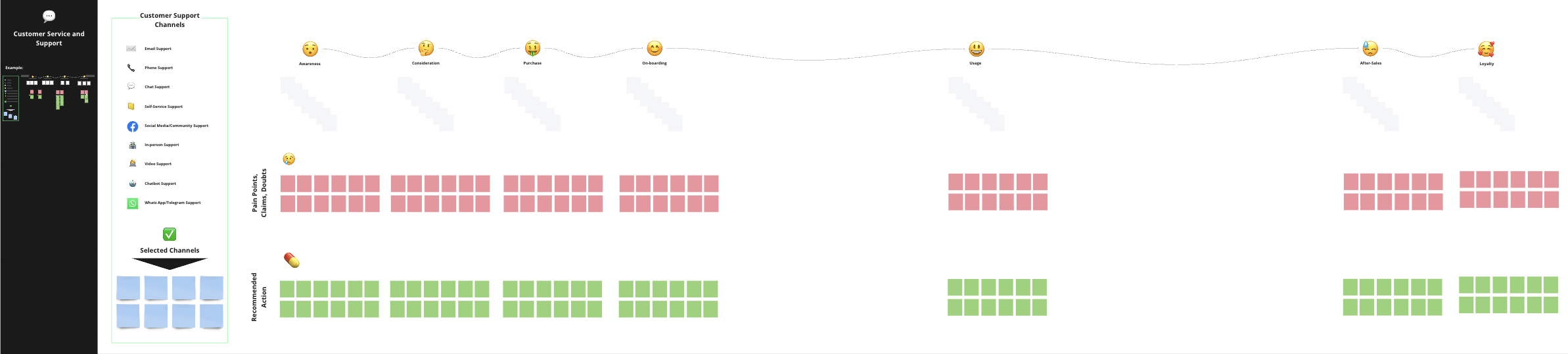
✅ So the first step will be to decide through which channel you will provide customer support. This mainly depends on the nature of your business model and/or product/service (the more complex your product, the likelier the need for personal interaction) and on your financial resources.
For new and smaller businesses, support via email and self-service will probably be a suitable option at least at the beginning.
If you decide to go for personal phone or chat support, you don’t necessarily have to hire your own customer support team. There are a number of companies out there which provide outsourced customer support services. Check for companies in your country and language. The same applies to chatbots, where you can also find AI-powered plug-and-play solutions out there.
Go to the second area of your Customer Experience Management 📒Template. Decide on the channel you will use and simply note down the selected channel on the blue post-its.
✅ In the next step we will identify the potential pain points, claims or doubts along the customer journey. And provide recommended actions for each pain point, which shall serve as a kind of playbook with guidelines for customer support.
For example a paint point could be a delay in the delivery of an order, and the corresponding action could be sending the customer an email before he can even complain, apologizing for the delay and providing a 20% discount on the next order as compensation.
- So go to your template and copy your customer journey interactions from the previous task.
- Then note down potential pain points, claims or doubts that could come up in the different stages on the red post-its.
- Once you’ve done that, use the green post-its and define the recommended action or sequence of actions for each of the identified points.
- Use the channel icons to indicate the support channel used for each recommended action.
- Finally you could also differentiate the recommended actions taking into account the customer segments you defined, especially the value segments. For example you can offer high value customers a higher compensation or you could provide an exclusive contact channel for high value customers.
Step D
Collect Customer Feedback

Another way of managing your customer experience is through collecting customer feedback. The feedback you collect from your customers can help to detect weaknesses in your customer experience which you can then work on improving
Measuring customer satisfaction is not a one-off thing, it should be monitored consistently and there are a number of ways in which customer feedback can be collected:
Solicited feedback – this is feedback that you collect proactively from your customer through any of the following tools:
- Customer Satisfaction Surveys: Surveys can be used to collect structured feedback from customers by asking specific questions about their experience with your product or service.
- Focus groups: Focus groups bring together a small group of customers to discuss specific topics related to your product or service in a more open-ended, qualitative way.
- User testing: User testing involves observing customers as they use your product or service to identify usability issues and get feedback on specific features or functions.
- In-app or on-page feedback: In-app or on-page feedback prompts can be used to collect feedback from customers while they are using your mobile app, software or website.
- Customer support interactions: Customer support interactions provide an opportunity to collect feedback from customers while they are actively engaged with your product or service.
Analyze unsolicited feedback – this is feedback that your customer leaves for example through reviews or social media usually without asking them to. You can also analyze this feedback to gain valuable insights:
- Customer reviews: Customer reviews provide valuable feedback on the customer experience with your product or service and can be analyzed to identify common themes and issues.
- Social listening: Social listening involves monitoring social media channels for mentions of your brand or product and can be used to identify customer sentiment and identify areas for improvement.
✅ So in the next step you want to define, when and how you will collect customer feedback. Therefore go to the third area of your Customer Experience Management 📒Template. Again copy all the customer touchpoints that you identified within your journey using the white post-its.
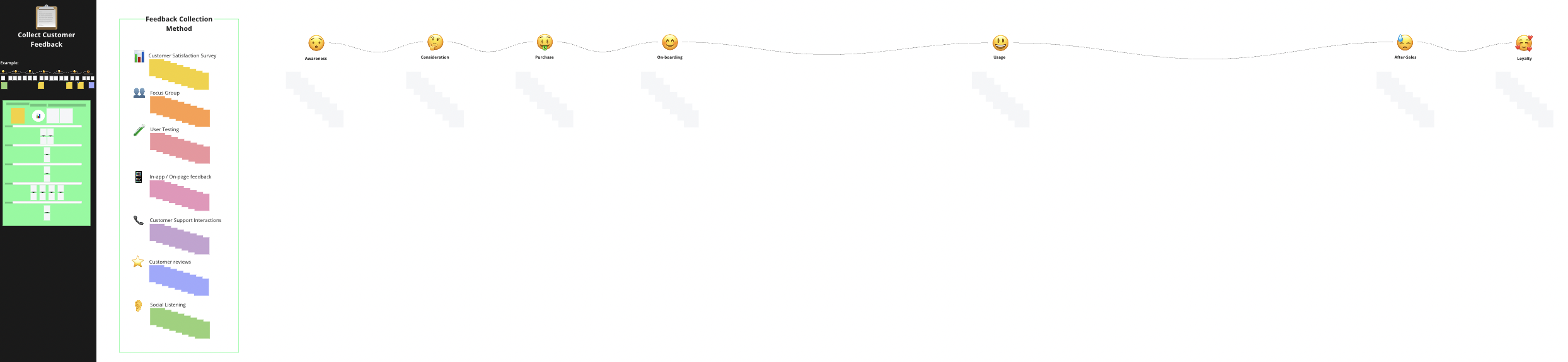
Then use the coloured post-its to define where, at which touchpoints, you will collect customer feedback.
- Choose the post-its color that corresponds to the feedback collection method you are using.
- Use the post-it to describe the way you will collect feedback and for which purpose.
- Place the post-it at the corresponding touchpoint within your customer journey.
Out of all the methods above, the customer satisfaction survey is probably the most common tool and at the same time the easiest one to implement especially for new and smaller businesses with little resources.
Once you have decided when you will collect feedback through which method, you will need to go a level deeper and define what type of solicited feedback you plan to collect in each moment, so the questions you will ask your customers.
A typical customer satisfactions surveys can include the following sections and questions:
Profiling Questions:
These questions can help you to confirm information about your customers or gather additional information. You could for example ask for demographic or geographic information. However, remember that the purpose of this survey is not to gather in-depth information on your customer themselves, but to evaluate their customer satisfaction. So keep this part reasonably short.
Example questions could include:
- What is your age range?
- What is your gender?
- What is your household income range?
- What is your occupation?
- Where do you live?
Net Promoter Score (NPS):
The NPS is a customer satisfaction metric that is commonly used to measure how likely customers are to recommend a product or service to others. The NPS survey usually asks customers to rate on a scale of 0 to 10, how likely they are to recommend the company/product/service to others. Based on their response, customers are then segmented into three categories:
- Promoters (score 9-10): Customers who are loyal and enthusiastic about the company and are likely to recommend it to others.
- Passives (score 7-8): Customers who are satisfied with the company but not necessarily loyal. They may consider alternatives in the future.
- Detractors (score 0-6): Customers who are unhappy with the company and may discourage others from using it.
Example questions could include:
- On a scale of 0-10, how likely are you to recommend our product/service to a friend or colleague?
Overall Customer Satisfaction:
The overall customer satisfaction is used to evaluate how satisfied the customers are with the company/product/service, as a whole. A common method to track this metric is to use a rating scale question, where customers are asked to rate their satisfaction with the company’s products or services on a scale of 1 to 10, or a similar numerical scale.
Example questions could include:
- On a scale of 1-10, how satisfied were you with your recent purchase?
- How would you rate the quality of our customer service on a scale of 1-10?
Customer Satisfaction with specific aspects:
You can then also go a level deeper and ask the customers about their satisfaction with individual aspects of your product/service/processes etc. This gives you valuable insight on what exactly works well and where improvement needs to be made. This information can be used to guide product development, marketing, and customer service efforts to better meet customers’ needs and preferences.
Example questions could include:
- Please rate your level of agreement with the following statement: “Our product/service met my expectations.”
- Please rate your level of agreement with the following statement: “Our customer service team was helpful and knowledgeable.”
- Did you find the checkout process easy to use? (Yes/No)
- Were you satisfied with the speed of delivery? (Yes/No)
- Which of the following features do you find most valuable in our product? (Ease of use/ Reliability/ Speed/Customizability)
Open Feedback:
Finally you can also ask your customers for open feedback.Those are questions that ask customers to provide written feedback in their own words, without any predefined response options. These questions can be helpful to gather additional detailed information on customer satisfaction, provide valuable insights into specific issues and uncover aspects of improvement you may not think of.
Example questions could include:
- What could we do to improve your experience with our product/service?
- Is there anything else you would like to tell us about your experience with our product/service?
💡 There are a number of different survey questions formats that you can use. You can find a survey question glossary amongst the Lists above.
✅ Now go again to the third area of your Customer Experience Management 📒Template and specify for each of the customer feedback collection activity that you defined the purpose and the questions you want to ask or the information you want to gain.
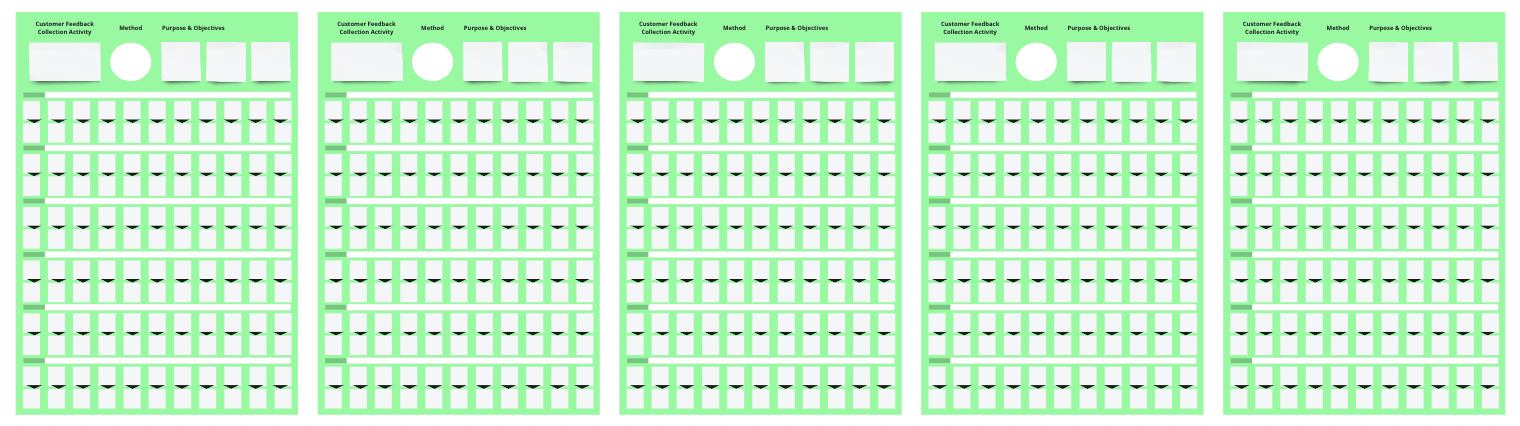
Remember less is more when it comes to surveys, customers are less likely to finish a survey that is too long. It’s best to keep customer surveys as short as possible, while still gathering the necessary information to meet your survey’s goals. Too many questions can lead to survey fatigue and a high dropout rate, which can negatively impact response rates and the quality of the data collected. A good rule of thumb is to keep customer surveys to around 10-15 questions or less. This allows for enough questions to gather relevant feedback while still keeping the survey short and manageable for respondents.
The same applies when using in-app/on-page feedback or user testing, keep it short and focused on what you really want to figure out at this moment in order to assure you will get more and higher quality responses.
And finally you will need to implement your customer feedback collections activity.
💡 There is a wide range of tools out there that you can use to start collecting feedback. For example customer survey tools for your customer satisfaction surveys, social listening tools to analyze feedback on social media or in-app feedback tools. We’ve put together a Customer Feedback Tools List which you will find above.
If you decide to go for the good ol’ customer survey, you can use for example google forms which is free and allows you to set up surveys and collect responses very economically.
Here is an example survey we build on Google Forms Go To Survey
Step E
Analysis and Experience Optimization

Once you collect the customer feedback you need to analyze it in order to understand your current performance in terms of customer satisfaction, extract insight, detect areas of improvement and optimize your customer experience.
Analyzing your customer feedback is again not a one of task but something that has to be done regularly to understand if the performance changed over time and how.
For example you could put together a customer satisfaction report on a monthly basis. This allows you to track the customer satisfaction over time, identify changes compared to the previous months or even year and understand the impact of any changes you make to your customer experience. For example if you added a new product feature or made a change in the pricing you can see if this had any impact on the customer experience.
On the other hand, let’s say you detect at some point that the overall customer satisfaction or NPS decreases. You can then look at the customer satisfaction of individual product/service aspects or check what your customers are saying in reviews or on social media, to understand what exactly causes the decrease in customer satisfaction. With this insight you can then move on to work on improving the experience again.
So we prepared a simple Customer Satisfaction Dashboard 📒Template which you can use to track your customer satisfaction by simply introducing your own data in the light green fields.
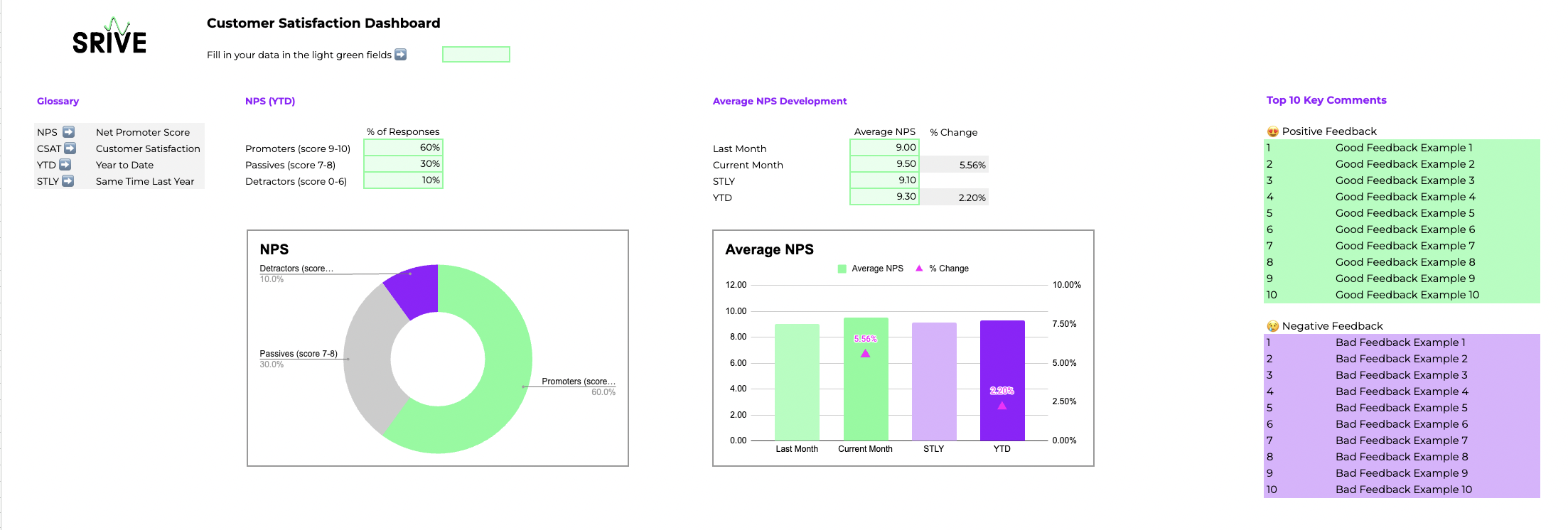

Here is a short explanation of each Metric.
NPS YTD
Introduce the your net promoter score data year to date:
- Promoters (% of respondents with a score 9-10)
- Passives (% of respondents with a score 7-8)
- Detractors (% of respondents with a score 0-6)
Average NPS
Introduce the your average net promoter score for the following time periods:
- Last Month (average NPS of the last month)
- Current Month (average NPS of the current month)
- STLY (accumulated average NPS at the same time last year)
- YTD (accumulated average NPS year to date)
Top 10 Key Comments
List the top 10 positive and negative customer comments you got from open feedback, customer reviews or social media comments.
Average Overall CSAT
Introduce the your average overall customer satisfaction for the following time periods:
- Last Month (average NPS of the last month)
- Current Month (average NPS of the current month)
- STLY (accumulated average NPS at the same time last year)
- YTD (accumulated average NPS year to date)
Average CSAT aspects/features
Introduce the your average customer satisfaction for each aspect/feature for the following time periods:
- Last Month (average NPS of the last month)
- Current Month (average NPS of the current month)
- STLY (accumulated average NPS at the same time last year)
- YTD (accumulated average NPS year to date)