Customer Relationship Model Guide
What is a Customer Relationship Model?
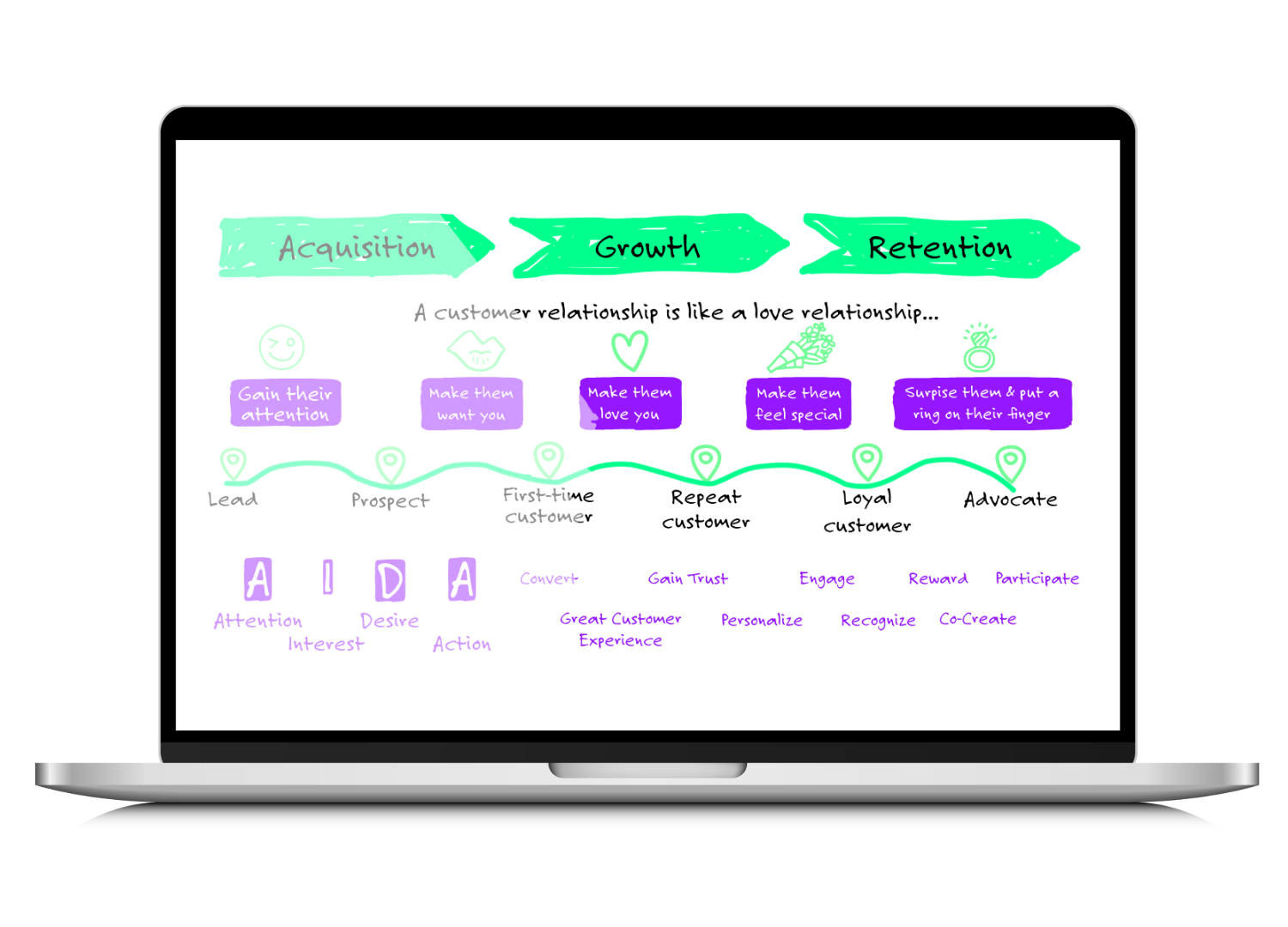
When we talk about a customer relationship model, we refer to the overall plan or strategy for managing one-on-one interactions with your customers with the goal of growing and retaining them. This customer relationship model can include both reactive and proactive interactions with your customers.
- Reactive activities involve a defined journey of interactions, such as sending personalized emails or targeted messaging that are launched based on certain triggers or alerts. For example, if a customer hasn’t placed an order in 6 months and moves from the “active” status to “sleeping,” this triggers a promotional email with the objective of reactivating the customer.
- Proactive activities involve a targeted plan of interactions per cluster, based on the specific objectives and characteristics of that cluster. The interactions are not triggered by a specific event but are sent to all customers within a cluster or segment at the same time.
At its core, a customer relationship model serves as the backbone of your customer engagement strategy, providing a systematic approach to nurturing relationships at every touchpoint of the customer journey. By leveraging both reactive and proactive interactions, businesses can tailor their communication to meet the unique needs and preferences of each customer segment, ultimately fostering loyalty, satisfaction, and long-term growth.
What is a Customer Relationship Model Good For?
A well-defined customer relationship model is crucial because it lays out a structured approach to nurturing and maintaining relationships with customers, leading to enhanced customer satisfaction, loyalty, and ultimately, business growth.
- Increased Customer Loyalty: By understanding and meeting the needs of your customers through personalized interactions, you can build stronger relationships and foster loyalty.
- Higher Customer Retention Rates: With proactive engagement strategies in place, you can reduce churn rates by consistently providing value and addressing customer concerns before they escalate.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: By anticipating customer needs and providing timely support and assistance, you can enhance overall satisfaction and positive brand perception.
Curated Lists 📋
💡 To save you some time, we have prepared a free list with CRM Tools which you can use to work on your customer relationship model.
How to Define Your Customer Relationship Model Step-by-Step:
Step A: Customer Relationship Model Template
Step B: Objectives per Cluster
Step C: Competitor Benchmark & Best Practices
Step D: Reactive Relationship Model
Step E: Proactive Relationship Model
Step F: Content Brief
Step G: Relationship Model Implementation
Step H: Activity Tracking and Metrics
Step A
Customer Segmentation Templates
To define your customer relationship model you can either create your own whiteboard template for example on Miro and use Google Sheets to build a CRM database and track your CRM activities or you can use our ready-to-use templates along with this guide.
Included Templates:

Customer Relationship Model Miro Board
CRM Database Spreadsheet Template
Relationship Model Tracker Spreadsheet
Step B
Objectives per Cluster

The first step is to define the objectives for each customer group or how we call them – cluster. A cluster is a group of customers or even of different customer segments that have selected characteristics in common. In the customer segmentation toolkit we explain step by step how to define your customer segments and clusters.
However, if you don’t want to go in detail right now simply try to divide your customers into meaningful clusters. Your various clusters likely differ for example in terms of geographic location, of customer value, activity status, or purchasing behavior. Therefore, the marketing and sales objectives to nurture and grow the customers of each segment will vary. So to define a suitable relationship model, you will need to clarify the clusters you serve and your objectives first.
The first step is to define the objectives for each customer group or how we call them – cluster. A cluster is a group of customers or even of different customer segments that have selected characteristics in common. In the customer segmentation toolkit we explain step by step how to define your customer segments and clusters.
However, if you don’t want to go in detail right now simply try to divide your customers into meaningful clusters. Your various clusters likely differ for example in terms of geographic location, of customer value, activity status, or purchasing behavior. Therefore, the marketing and sales objectives to nurture and grow the customers of each segment will vary. So to define a suitable relationship model, you will need to clarify the clusters you serve and your objectives first.
✅ To define your objectives, go to the first section of your Customer Relationship Model 📒Template, note down your customer clusters (as described above), and define the objectives you plan to reach for each cluster. Those objectives could include, for example:
- Lock in new customers
- Retain active customers
- Reactivate sleeping customers
- Prevent churn
- Recover lost customers
- Increase average order value
- Maintain average order value
- Increase purchase frequency
- Maintain purchase frequency
- Increase customer lifetime value
- Up-sell to a higher-value product
- Cross-sell to other products
- Increase customer engagement
- Generate referrals
- and so on.
Step C
Competitor Benchmark & Best Practices

Before starting to work on your own relationship model, gather inspiration and collect ideas by examining what your competitors and businesses in other industries do. What type of one-on-one communications do they send, and through which channels?
✅ Use the second section of your Customer Relationship Model 📒Template to record your findings. Check your email inbox and mobile notifications to see what type of communications you receive from other brands. Sign up for your competitors’ newsletter, create a profile on their online shop, or download their app to see what type of messages and notifications you receive. Take screenshots, copy images or links of noteworthy communications, and add them to your template.

Step D
Reactive Relationship Model

Now, let’s start working on your “reactive” relationship model.
A reactive relationship model is a plan where you initiate a defined journey of interactions with a customer only after certain triggers or alerts have been identified. In this approach, you are still reacting to specific events or actions taken by the customer, but you are doing this based on a predefined plan or set of activities in place to respond to these triggers.
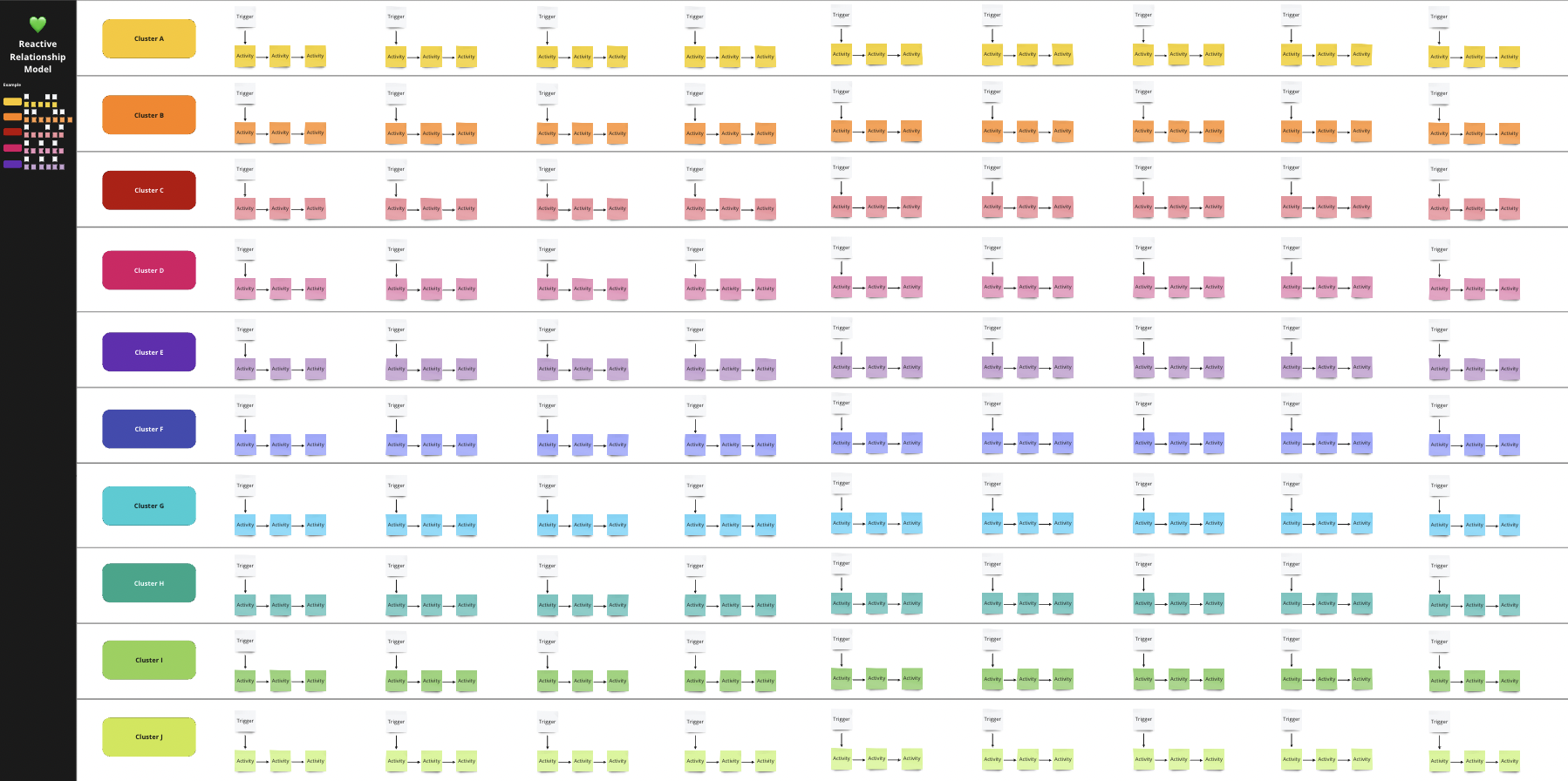

✅ Identify the Triggers: To start defining your reactive relationship model you will need to identify the different triggers.
Triggers refer to specific events or actions taken by a customer that signal a need for engagement or intervention from your side. These triggers could include a customer not making a purchase in a certain amount of time, a customer reducing the average order value or action that indicates a need for engagement.
So go to your Customer Relationship Model 📒Template and use the third area to define the different trigger events for each of your clusters using the white post-its.
✅ Define the Activities:
Once you identify the triggers, you can launch a defined journey of interactions, such as sending personalized emails or targeted messaging, to try and re-engage or grow the customer or make them take another specific action. These reactive activities are designed to help keep the customer engaged or retain them, increasing customer satisfaction and loyalty and growing their value.
For example if a customer hasn’t placed an order in six months, they may be moved from an “active” status to a “sleeping” status in your customer database, which triggers a promotional email with the objective of reactivating the customer.
Types of reactive activities could, amongst others, include:
- Personalized email campaigns: You could send targeted emails to customers based on their interests, past purchases, or other behaviors.
- Promotions and discounts: If a customer hasn’t made a purchase in a certain amount of time, you could offer them a discount or promotion to encourage them to make a purchase.
- Proactive customer service: If a customer expresses dissatisfaction with a product or service, you could proactively reach out to them to address their concerns and offer a solution.
- Upselling or cross-selling: If a customer makes a purchase, you could offer additional products or services that complement the purchase they’ve already made.
- Loyalty program incentives: If a customer is on the cusp of reaching a loyalty program milestone, you could offer incentives or rewards to encourage them to make a purchase and reach the milestone.
- Abandoned cart reminders: If a customer adds items to their online shopping cart but doesn’t complete the purchase, you could send them a reminder email or message with a call to action to complete the purchase.
- Product recommendations: Based on a customer’s past purchase history or browsing behavior, you could send them personalized product recommendations that they may be interested in.
- Service reminders: If a customer has a subscription or recurring service, you could send them reminders to renew or schedule their next service appointment.
- Birthday or anniversary messages: You could send personalized messages to customers on their birthday or the anniversary of when they first became a customer.
- Surveys or feedback requests: After a customer completes a purchase or service, you could send them a survey or request for feedback to gather insights and improve the customer experience.
Again, use your Customer Relationship Model 📒Template to specify the corresponding activities that you want to launch for each trigger that you define, these could be single activities or a sequence of activities.. This time use the colored post-its to note down the activities.
Consider that probably the most efficient and at the same time economic channel to interact with your customers will be through email. We will look into how to use email to implement your relationship model later in more detail. Of course other ways of reaching out could be through phone, via social media direct message, SMS, messenger or through notifications if you are offering a mobile app. However, those are generally speaking more costly, more complicated to implement or require more manual work. So if your business is at an early stage email will be the most appropriate choice.
Step E
Proactive Relationship Model

Next, you also want to develop your proactive relationship model, an annual plan of campaigns consisting of one-on-one marketing and sales activities based on the objectives of each cluster. Unlike reactive activities that are triggered by specific events, proactive activities are not necessarily tied to a particular trigger event but are part of an overall plan that is executed for all clients in a cluster at the same time.
In order to be effective, the activities and their content should be targeted to each cluster considering characteristics such as their status or lifecycle stage, value, as well as demographics and geography.
There is a wide range of activities that you can include in your one-on-one plan. Here are some examples:
|
Activity Type |
Example Activities |
|
Cross-selling |
|
|
Up-selling |
|
|
Increase Customer Engagement |
|
|
Increase Purchase Frequency |
|
|
Increase Average Value or CLV |
|
|
Customer Retention |
|
|
Avoid Churn |
|
|
Reactivate Sleeping Customer |
|
|
Recover Lost Customer |
|
|
Educate/On-board Clients |
|
|
Increase Customer Satisfaction |
|
|
Reward Loyal Customers |
|
|
Event/Season Based Activities |
|
|
Location/Geographic Activity |
|
|
Demography Based Activity |
|
✅ Now go ahead and use the fourth area of your Customer Relationship Model 📒Template to lay out your one on one activity plan for each of the clusters.
Consider that here as well email will probably be the most logical channel to use for the reasons mentioned above.

Step F
Content Brief

Finally create a very short content brief for each activity.
A content brief outlines the details and specifications for the individual activity. It provides a framework for your marketing team when it comes to creating the content and executing the activity.
When it comes to one on one activities such as the ones you have defined in the context of your relationship model, it is essential to segment and personalize your content.
Segmented content refers to content that is tailored to specific segments of your audience, based on factors such as status, value, demographics, location, or behavior. This allows for more targeted messaging that resonates with each group, which can increase the activity’s efficiency.
Personalized content takes segmentation one step further by creating content that is customized to an individual customer. This can include using their name in an email, recommending products based on their purchase history, or tailoring messaging based on their behavior on your website or social media channels.
✅Use the fifth area of your Customer Relationship Model 📒Template to define a short brief for each activity by specifying the following elements:
- Name the activity.
- Choose the activity type (reactive or proactive).
- Note down when this activity is launched. So either the trigger for reactive activities or the launch date for proactive activities.
- Note down the cluster(s) this activity is directed to.
- Describe the key content elements of the activity, so what you are planning to offer or include in this activity.
- Specify the key message of this activity, meaning the main point that you want to communicate to your target audience through the activity. The key message is typically developed based on the campaign objectives and the target audience’s needs, wants, and pain points in order to resonate with the specific target audience (cluster) of this activity.
- Specify the Call to Action (CTA) that you plan to include in this campaign based on the action you would like the customer to take. A CTA typically takes the form of a button or link and includes a directive verb or phrase, such as “Buy now,” “Sign up today,” or “Learn more.”
- Specify again the key objective of this activity
- And finally list all the content personalizations. Meaning all the individual content elements that you will personalize for individual customers. For example their name, the product offer etc.

Step G
Relationship Model Implementation

To implement your relationship model you basically need two things: a CRM to manage your customers and an email marketing tool to implement and launch your activities in the form of email marketing.
💡 Remember, we’ve put together a List with CRM and Email marketing tools above
CRM
A CRM (Customer Relationship Management) tool is a software application that helps you to manage your interactions with your customers. Those tools are designed to help you stay organized and efficient in your customer interactions by keeping track of customer data and communication history and even automating certain tasks, and providing insights and analytics to inform business decisions.
There is a huge variety of CRM tools out there that come at different costs, some of which even offer email marketing functions. You will find a number of CRM tools on the list above. The more customers you have in your database the larger the need for a proper CRM tool to reduce manual tasks.
However, we of course also provide a low cost option in the form of a CRM Database 📒Template that you can use and that will be just fine if you are still at an initial stage with a manageable number of customers.
Remember you can get it here.
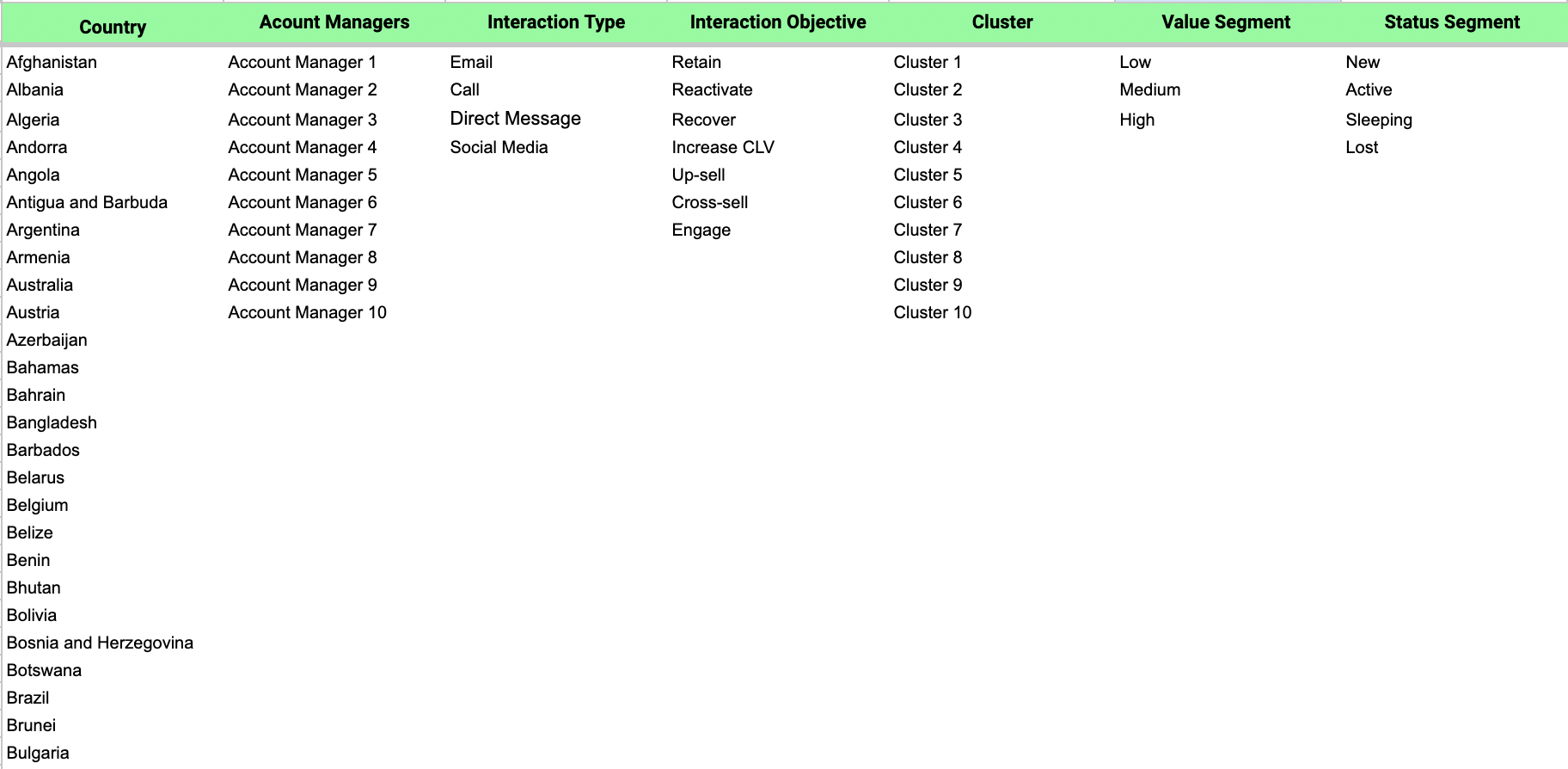
In the CRM you will basically find 3 tabs:
🗃️ The Variables Tab: Here you can introduce the lists of variables such as the names of your account managers, the names of the clusters, value segments and status segments you defined and any other variables that you want to include in your CRM database.
🗃️ The B2C/B2B CRM Tab: Here you can add your clients (1 line per client) and enter their corresponding information. The variables are very similar to the ones you can find in your customer segmentation database, however, you will find some new fields under segments changes and interactions.
Use those fields to keep track of any changes in the customer’s cluster, value or status segment as well as past interactions. Those fields will be essential for planning the next best reactive interactions.
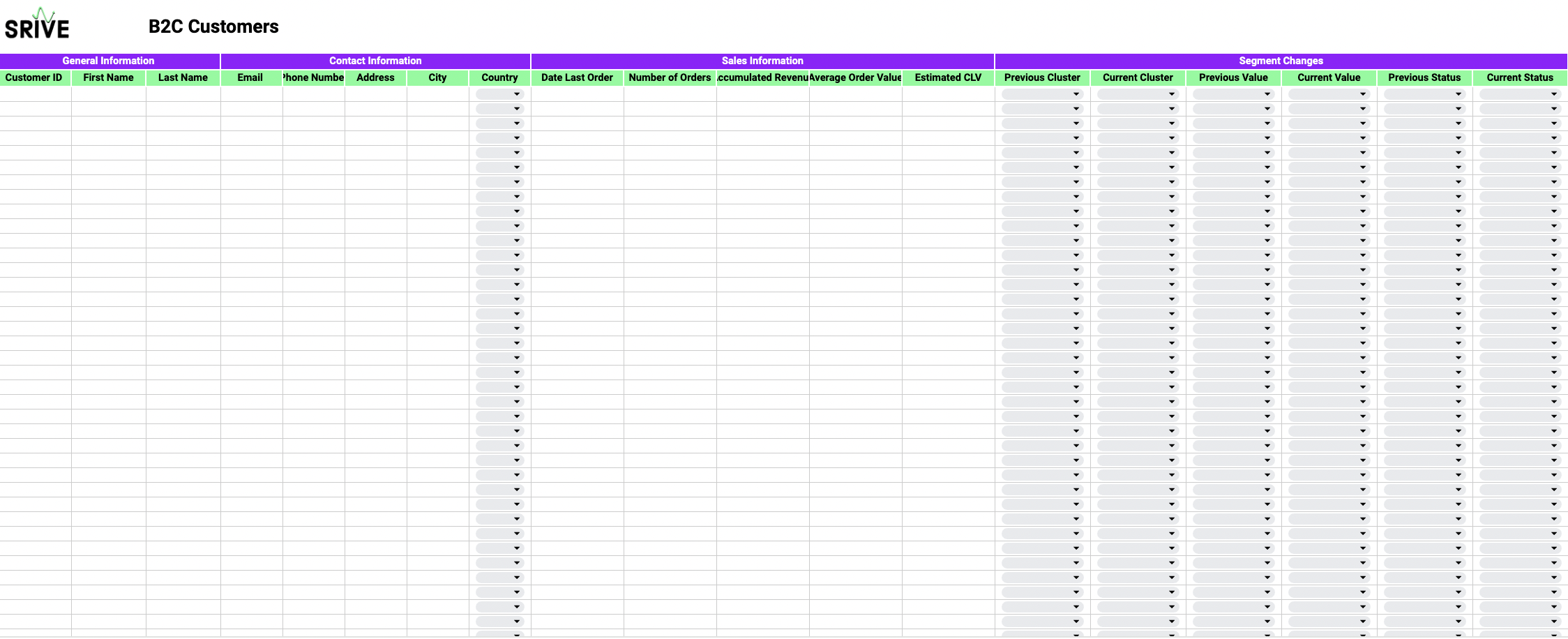
🗃️The B2C/B2B Interaction Tab: you can use this table to keep track of ALL your customer interaction if you want to do so. By simply entering the information on every interaction. (1 line per interaction).

Email Marketing Tools
On the other hand there are the email marketing tools, some of which even offer CRM functions. Email marketing tools are software platforms designed to help you create, send, and manage email campaigns. These tools typically include features such as email templates, list management, segmentation, automation, A/B testing, analytics, and reporting.
There is a huge variety of email marketing tools out there and most of them offer a free version that is sufficient for businesses with a smaller customer. You will find some email marketing tools on the list above.
Each email marketing tool works a little differently of course, and we recommend you to familiarize yourself with the tool you decide to use through their own tutorials.
However, generally speaking the process to use most email marketing tools would be as follows:
- Sign up and create an account with the email marketing tool provider.
- Import your email list or create a new one.
Set up a campaign:
- Design your email template or use a pre-designed template.
- Create the content for your email, including subject line, body copy, and images.
- Personalize your email content if desired, using information from your email list.
- Preview and test your email to ensure it appears correctly and is error-free.
- Schedule or send your email campaign to your email list.
- Track and analyze the results of your campaign, including open rates, click-through rates, and conversions.
- Use the insights gained from your analysis to optimize your future email campaigns.
Set up an email automation flow:
- Identify the trigger event that will start the email flow, such as a new subscriber, a specific action taken by the subscriber, or a certain date or time.
- Define a series of emails that align with your goal and trigger event. Each email should be designed to move the subscriber closer to your goal, whether that’s making a purchase, scheduling a consultation, or downloading a resource.
- Design your email templates or use a pre-designed template.
- Create the content for each email, including subject line, body copy, and images.
- Set up the automation flow in your email marketing tool, specifying the trigger event and the sequence of emails to be sent.
- Test the automation flow to ensure that it is functioning as intended.
- Launch the automation flow and monitor its performance, making adjustments as needed to improve results.
Step H
Activity Tracking and Metrics

And last but not least you want to keep track of your reactive and proactive activities to see how they are performing, which ones work well, which ones don’t to make the necessary adjustments to keep improving your relationship model.
Most email marketing tools include some kind of analytics dashboard that allows you to track the most important KPIS of your activities. However we also provided a Relationship Model Tracker 📒Template which you can access here.
✅ Use the 🗃️Variable Tab to define your variable fields:
- Introduce the starting date
- Introduce the names of your team members
- Define the activity types (you can also just leave the current ones)
- Define the the activity objectives (you can also just leave the current ones)
- Introduce your clusters that you defined earlier
✅ Use the 🗃️Activity Tracker Tab to keep track of all your activities. Introduce each activity and fill out the activity details. Define the type of metrics you want to use to track your activity performance and introduce them in header, then define the target numbers for each activity. When executing the activities regularly update the metric actuals in the spreadsheet.
Common metrics to track one on one activities via email include:
- Customer reached: Number of customers that received the email.
- Open rate: The percentage of emails that were opened by recipients.
- Click-through rate (CTR): The percentage of recipients who clicked on a link within the email.
- Conversion rate: The percentage of recipients who completed a desired action, such as making a purchase, after clicking on a link within the email.
- Unsubscribe rate: The percentage of recipients who opted out of future emails.
- Bounce rate: The percentage of emails that were undeliverable, either because the recipient’s email address was invalid or because the email was blocked by the recipient’s email provider.
- Spam complaint rate: The percentage of recipients who marked the email as spam.
- Revenue generated: The total amount of revenue generated from the email campaign.
- Return on investment (ROI): The amount of revenue generated compared to the cost of the email campaign.