Website & Online Shop Creation Guide
What Does Website & Online Shop Creation Comprise?
No matter if you are selling a tech or non-tech product or service, your business is unlikely to survive without some kind of website or online-shop.
Creating a website to represent your brand online, will enable you to:
- Establish an online presence: In today’s digital age, your website is often the first point of contact between your business and your potential customers. Having a website or online shop helps your business establish an online presence and allows potential customers to find and learn more about it.
- Provide information to customers: Through your website or online shop you can provide information to customers about the products or services you offer, business hours, location, contact information, and more. This information can help customers make informed purchasing decisions.
- Build credibility and trust: A well-designed and professional-looking website can help your new business build credibility and trust with potential customers. It shows that the business is legitimate and takes its online presence seriously.
- Enable online sales: An online shop allows your business to sell its products or services to customers who may not be able to visit the physical store. It also provides a convenient way for customers to make purchases from the comfort of their own homes.
- Increases visibility: Your website or online shop can help your business increase its visibility online, making it easier for potential customers to find the business through search engines and social media
Also, an online channel provides new businesses with access to a larger audience, lower marketing costs, increased flexibility, real-time data and insights, and online sales opportunities. Creating a website or online shop is essential for any new business looking to establish a strong brand presence and grow its customer base.
So, if you have the budget, the easiest, of course, is to hire a web designer to help you build your website or online shop. If not, don’t worry, even someone without any coding experience can build a website or online shop using one of the many drag and drop website builders out there. We will have a look at them in a moment, but let’s move through all the important points step by step.
Note: 🍋 Throughout this guide we will use the example of a food supplement company to better illustrate each task and information.
Why Is It Essential To Have a Website or Online Shop?
No matter if you are selling a tech or non-tech product or service, your business is unlikely to survive without some kind of website or online-shop. Creating a website to represent your brand online, will enable you to:
- Establish an online presence: In today’s digital age, your website is often the first point of contact between your business and your potential customers. Having a website or online shop helps your business establish an online presence and allows potential customers to find and learn more about it.
- Provide information to customers: Through your website or online shop you can provide information to customers about the products or services you offer, business hours, location, contact information, and more. This information can help customers make informed purchasing decisions.
- Build credibility and trust: A well-designed and professional-looking website can help your new business build credibility and trust with potential customers. It shows that the business is legitimate and takes its online presence seriously.
- Enable online sales: An online shop allows your business to sell its products or services to customers who may not be able to visit the physical store. It also provides a convenient way for customers to make purchases from the comfort of their own homes.
- Increases visibility: Your website or online shop can help your business increase its visibility online, making it easier for potential customers to find the business through search engines and social media
Also, an online channel provides new businesses with access to a larger audience, lower marketing costs, increased flexibility, real-time data and insights, and online sales opportunities. Creating a website or online shop is essential for any new business looking to establish a strong brand presence and grow its customer base.
Curated Lists 📋
💡 To save you some time, we have put together a free list with Website Creation Tools, a free list of Website Plugins and a free list of SEO Tools which will be helpful when creating your website or online shop.
How to Build Website or Online-Shop Step-by-Step:
Step A: Hosting, Domain, SSL & CMS
Step B: Website Structure & Wireframe
Step C: Web & UI Design
Step D: Website Set-up and Plugins
Step E: SEO Optimization
Step A
Hosting, Domain, SSL & CMS

Before being able to create a beautiful user interface in the front-end, you will need to set up your back-end on which your website or online shop will run. I know, for all the non-tech founders out there that already sounds pretty techy and complicated, but don’t worry there are numerous plug and play solutions out there that make this step very easy. And in the following we will explain all these concepts in detail and words everyone understands.
Hosting
First of all you’re gonna need hosting for your website. Hosting refers to the process of storing a website or web application on a server so that it can be accessed by users over the internet. When someone wants to access a website or web application, their computer sends a request to the server where the website is hosted. The server then sends back the website’s files, which are displayed on the user’s device as a web page.
There are different types of hosting. Which one you choose heavily depends on the type and size of your business operations.
- Shared hosting: Shared hosting is a type of hosting where multiple websites are hosted on a single server. This means that resources such as CPU, RAM, and storage are shared between all the websites hosted on that server. Shared hosting is the most common type of hosting and is suitable for small websites or blogs with low traffic. Shared hosting plans are typically affordable and easy to set up, making them a popular choice for beginners.
- VPS hosting: VPS stands for Virtual Private Server. VPS hosting is a type of hosting where a physical server is divided into multiple virtual servers. Each virtual server has its own dedicated resources such as CPU, RAM, and storage. VPS hosting provides more resources and control over the server than shared hosting, making it suitable for websites with moderate traffic or resource-intensive applications. VPS hosting plans are typically more expensive than shared hosting but offer better performance and scalability.
- Dedicated hosting: Dedicated hosting is a type of hosting where a business or individual rents an entire physical server for their exclusive use. With dedicated hosting, the customer has full control over the server and can configure it to meet their specific requirements. Dedicated hosting provides the highest level of performance, security, and customization but is also the most expensive type of hosting. It is suitable for high-traffic websites or web applications with specific requirements that cannot be met by shared or VPS hosting.
- Cloud hosting: Cloud hosting is a newer type of hosting that provides scalable resources and high availability. With cloud hosting, a website or web application is hosted on a network of interconnected servers instead of a single physical server. This provides greater scalability, as resources can be added or removed as needed. Cloud hosting also provides high availability, as websites and web applications are hosted on multiple servers, reducing the risk of downtime. Cloud hosting plans are typically more expensive than shared or VPS hosting, but offer better performance and scalability.
Hosting providers offer services to store and maintain websites and web applications on their servers. These providers typically offer a range of hosting plans including plans for the above mentioned hosting types and with specific plans for wordpress hosting (wordpress is the most common content management system, we will talk about CMS in a moment) and for e-commerce.
So the first thing you want to do is to choose a hosting provider. Which providers are available to you depends on where in the world you are located in the world.
You will find a number of the largest international hosting providers that are available in various countries on your Website Creation Tools List.
Domain
The next step would be to choose your domain name. A domain is a unique name that identifies your website on the internet. It’s like the address of a house, but for a website. A domain name consists of two parts: the name and the extension. For example, in the domain name “google.com,” “google” is the name and “.com” is the extension.
A domain name is used to help people find and remember websites. When someone types a domain name into their web browser, it sends a request to the internet’s domain name system (DNS), which looks up the IP address associated with that domain name. The IP address is the unique identifier for the server where the website is hosted, and the browser uses it to connect to the website and display its content.
Domain names are registered with domain name registrars, which are companies that manage the registration and allocation of domain names. When you register a domain name, you can choose from a variety of extensions, such as .com, .org, .net, and many more. The availability and cost of domain names can vary depending on the extension and the popularity of the name.
When selecting your domain name keep the following in mind:
- Keep it short and simple: A domain name that’s easy to remember and type can help your visitors find your website more easily.
- Make it easy to spell: Avoid using complicated or unusual spellings that could confuse your visitors.
- Use relevant keywords: Including relevant keywords in your domain name can help with search engine optimization (SEO) and make your website easier to find.
- Choose a memorable name: A catchy or unique name can make your website stand out and be more memorable to visitors.
- Avoid numbers and hyphens: Numbers and hyphens can make your domain name harder to remember and type.
- Consider your brand: If your domain name is also your brand name, make sure it accurately reflects your business and its values.
- Consider the extension: Choose an extension such as .com, .org, or .net. that’s appropriate for your website or business, consider for example the country market you are in.
- Check for availability: Use a domain name registrar or search engine to check if the domain name you want is available. You can also try different extensions in case your first option is not available.
Most of the original hosting providers also offer domain name check and registration services, actually a lot of the plans include a free domain. However, there are also a number of domain name registrars and marketplaces that focus on offering domains. Here you can check, purchase and register domains which you can then connect in a second step with your website. You will find a number of providers on your Website Creation Stack 📋List.
SSL
You also want to make sure to protect the security and privacy of your through a SSL Certificate. A SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificate is a digital certificate that authenticates the identity of a website and encrypts the data that is sent between the website and its users. It helps to ensure that sensitive information such as passwords, credit card numbers, and other personal data cannot be intercepted by hackers or other malicious actors.
When a website has a SSL certificate, it uses HTTPS (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secure) instead of the standard HTTP protocol. HTTPS creates a secure connection between the website and the user’s web browser, using a process called encryption. This means that any data that is sent between the website and the user is protected and cannot be read or modified by unauthorized third parties.
SSL certificates are issued by trusted third-party organizations called Certificate Authorities (CAs). To obtain a SSL certificate, a website owner must provide the CA with proof of their identity and ownership of the domain name. Once the SSL certificate is issued, it can be installed on the website’s server, enabling HTTPS and providing a secure connection for users.
Most hosting plans also include a SSL certificate or you can purchase it in addition to your plan from your hosting provider. If you are new to the whole website building thing we would definitely recommend purchasing the SSL certificate through the same hosting provider. Since all you have to do then, once you set up your website hosting, is click a button and activate the SSL certificate.
Content Management System (CMS)
A CMS (Content Management System) is a software application that enables you to create, manage, and publish digital content, typically for a website, without needing specialized technical skills or knowledge of programming languages.
A CMS typically includes a user-friendly interface for creating and editing content, as well as tools for organizing and managing content, such as a database to store content and media files. Some common features of a CMS include:
- WYSIWYG (What You See Is What You Get) editor: a visual editor that allows users to create and edit content without needing to write HTML or other code.
- Media management: tools for uploading, storing, and managing images, videos, and other media files.
- Templates and themes: pre-designed templates and themes that can be used to customize the look and feel of a website.
- User management: tools for managing user accounts and permissions, allowing different users to have different levels of access and editing capabilities.
- Analytics and reporting: tools for tracking and analyzing website traffic and user behavior.
- Search engine optimization (SEO) tools: features that help optimize content for search engines, such as meta tags and friendly URLs.
The probably most used and popular website builder and CMS is WordPress, with a huge number of third party themes and plug-ins that you can add to your WordPress site to achieve additional functionalities.
And then there are e-commerce CMS platforms that allow you to easily create and manage online shops or other e-commerce sites to sell online. One of the most popular ones is Shopify.
You will find a number of website builders and CMS on your Website Creation Stack 📋List.
Step B
Website Structure & Wireframe

Website Structure
Once you set up the backend of your website or online shop and before going all in building and designing your site or shop, we recommend you to lay out the organization and structure (Sitemap) of your site first and create a wireframe that serves as the blueprint for your website.
We have prepared a 📒Template that you can use to define your site’s organization and structure. It has an example structure for a typical website and online shop that you can use as a basis to modify and add pages or sections according to your needs.
Website & Online Shop Creation Templates
To define your website structure and create your website or online shop wireframe you can either build your own templates for example on Miro or you can use our ready-to-use templates along with this guide.
Included Templates:

Site Structure Miro Board

Website Wireframe Miro Template

Online Shop Wireframe Miro Template

Mobile Wireframe Miro Template

Your website or online shop should have a logical intuitive structure. So, when defining the structure of your website put yourself in the shoes of your user and image how they would navigate your page and consider the page hierarchy:
- Identify the Main Navigation Points: These are the primary categories or sections of a website that are listed in the main navigation menu. They represent the main areas of content or functionality on the site and serve as the top-level organization for all of the site’s pages and sections.
- Define the Home Page and Landing Pages: This is the main entry point of a website and the first page that users typically see. It serves as the primary introduction to the website and often contains key information, such as an overview of the site’s content or functionality, links to the main navigation points, and calls-to-action. You could have different landing pages, depending on the channel through which someone enters your page.
- Organize your Pages into Parent Pages: This is a page that has sub-pages underneath it. Parent pages help to organize related content and create a clear hierarchy on the website.
- Define the Sub-Page Which goes Underneath: These are pages that are linked to from parent pages or other pages on the site. They provide more detailed information on a particular topic or sub-category within a parent page, and may also have their own sub-pages.
- Divide your Pages into Page Sections: These are individual sections or blocks of content within a page that are often separated by headings or other visual cues. They may contain text, images, videos, forms, or other types of content, and are used to organize and present information in a structured and easily digestible format. Page sections may also be used to break up long pages into smaller, more manageable chunks.
Wireframe:
Based on this structure you can now create your Wireframe and design the user experience of your website or online shop.
A wireframe is a visual representation of the basic layout and structure of a web page or application. It is essentially a simplified blueprint or schematic that shows the placement of elements on the screen and the overall user interface design, without getting into specific details of colors, images, or fonts. Wireframes help to plan and visualize the layout of the content and user interface before investing time and resources in more detailed design work. It typically focuses on the placement of key features and interface elements such as navigation, buttons, forms, and text.
When creating your wireframe you always want to keep the user, his needs, behavior and preferences in mind. By doing so, you make sure to provide a positive user experience and a website or online shop that is easy to use, functional, and enjoyable to interact with.
You can use the wireframe to communicate design ideas and collaborate with your team members, as they allow for quick iteration and feedback on layout and functionality. They can also help identify potential usability issues or design problems early on in the design process, saving time and resources in the long run.
As mentioned earlier, we’ve prepared three wireframe templates that you can adjust to lay out your pages, the page sections and individual page elements. You can find more placeholders to represent different website elements in your Miro wireframe library (check your template for the indications).
Website Wireframe
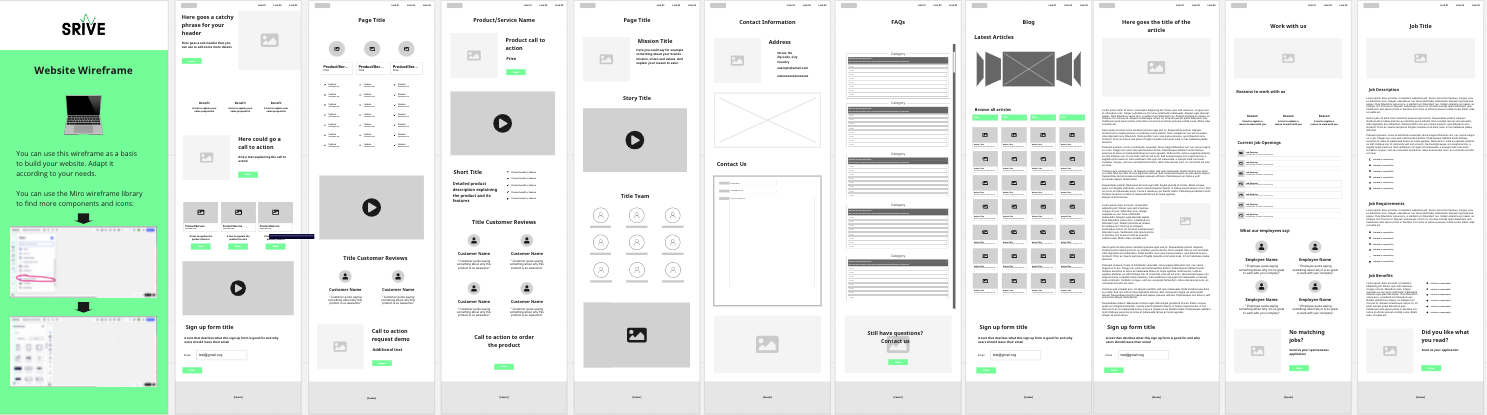
Online Shop Wireframe
Mobile Wireframe
Step C
Web & UI Design

Once you are clear about your website structure and layout, you can start working on your website frontend and start designing your website and UI (User Interface).
Web(site) design refers to the process of creating the visual layout, structure, and overall look and feel of a website. You can use design tools and theme editors to create a website’s visual elements, including typography, color scheme, layout, and graphics.
UI (User Interface) design refers to the design of the user interface elements of a website or application, such as buttons, icons, and other interactive elements that allow users to interact with the website or app. The UI designer is responsible for ensuring that the website or app is easy to use, intuitive, and visually appealing.
There are a number of website and online shop builders out there that you can use to create and design your website or online shop. In our humble opinion there are two large camps, one is WordPress and then there are the “all-in-one” website or online shop builders.
|
WordPress |
All-in-one builders |
|
|
Description |
WordPress is probably the most used CMS and website builder in the world. You can use wordpress with thousands of plugins that you can download to add more functionalities to your site. We will have a more detailed look into different types of wordpress plugins in the next chapter. While WordPress as a CMS itself is free, you will have to pay for hosting, your domain and other paid plugins offered by third party providers. | Website and e-commerce builders like Wix, Shopify, Squarespace or Webflow are platforms that allow users to create and manage their own websites without the need for extensive technical skills or knowledge of coding. These platforms typically provide an all-in-one solution for creating a website, including website templates, drag-and-drop editors, hosting, domain registration and support. Those builders are usually paid, though some offer free versions to build a site, you will usually have to pay once you want to publish your site under your domain. |
| Design | Now when it comes to designing your wordpress site there are a number of options. You can just buy a pre-designed theme that you like and install it on your wordpress site, you can find those themes on marketplaces like Theme Forest or Template Monster. Then there are theme & page builders, like the Divi builder and Elementor. Those come with a library of pre-designed themes that you can personalize and edit according to your taste, using their simple to use drag and drop editors without having any coding skills. |
In terms of design, most all-in-one builders offer a range of templates and themes that businesses can choose from to design their website and pages. These templates and themes are pre-designed and customizable to meet the specific needs of the business. They usually also come with drag-and-drop page builders that allow businesses to easily create custom pages without coding. These tools typically provide a range of modules and elements that can be added to pages, such as text, images, videos, and forms. |
| Ecommerce |
Now, if you are planning to build an online shop with wordpress, you will need an e-commerce platform plugin like for example WooCommerce. E-commerce platforms allow you to:
E-commerce plugins allow you to add those functionalities to your website without any coding skills. |
Within this range of website and e-commerce builders, exist solutions that are specialized e-commerce platforms, with Shopify probably being the most popular example. However, most of the all-in-one builders offer e-commerce capabilities such as:
E-commerce builders are easy to use also for non-tech founders and let you set up a decent online-shop quite quickly. |
| Membership Management |
Finally, if you are planning to offer some kind of subscription or membership based business model, you will need a membership management plugin like for example Memberpress. Those type of plugins allow you to:
|
There are also specialized all-in-one solutions, if you are building a subscription or membership based business. A popular example is Memberstack. Besides including a website builder those platforms come with specialized features like:
In summary those solutions allow you to create your own membership or subscription service platform without the need of coding skills. |
| Advantages |
|
|
| Disadvantages |
|
|
So which website builder you choose depends largely on the business you are building and your tech skills. You will find a range of tools in all those categories on your Website Creation Stack 📋List.
Choose or build your theme and design your UI:
Once you select your website or shop builder it is time to start creating. So the first thing you want to do is to choose or build your theme.
A website theme is a collection of design elements and templates that determine the visual appearance of a website. It includes the layout, color scheme, typography, and other design elements that are used to create the overall look and feel of the website. A website theme can be thought of as a pre-built design that can be applied to a website to give it a specific style and aesthetic. Most of the website builders offer a variety of pre-built themes that you can choose from and apply to your website.
You can then adapt the layout, color scheme, typography and other design elements to your brand design and include your logo, images and other graphic elements that represent your brand image and help to visualize your offering. When building or adapting your theme you should consider the following:
- Consider the website’s purpose: The website theme should align with the website’s purpose and convey its message clearly.
- Choose appropriate colors: Use colors that complement the website’s purpose and are consistent with the brand identity.
- Use a responsive design: Ensure that the website theme is optimized for different screen sizes and devices, like tablet or mobile screens.
- Prioritize readability: Use a font that fits the brand design and the website’s purpose but which is also easy to read. Ensure there is adequate contrast between the text and the background.
- Create a consistent layout: Consistency in layout, typography, and imagery helps establish a cohesive theme and brand identity.
- Use appropriate imagery: Use high-quality and relevant images, illustration and graphics that complement the theme and the website’s purpose.
- Keep it simple: A simple theme is easier to navigate and more user-friendly.
- Use iconography wisely: Icons are a universal language that transcends cultural and language barriers, making them a powerful tool for communication in UI designUse icons to convey meaning and provide visual cues to users. Ensure that the icons are recognizable, and their meaning is clear.
- Make sure navigation is intuitive: Use intuitive navigation to guide users through the interface and make it easy for them to find what they are looking for. Use clear and descriptive labels for navigation items. Ensure that the buttons are placed in prominent locations and are easy to click on. Place important elements such as navigation, search bar, and calls to action in prominent locations.
We won’t dive into detail on how to use the various theme and page builders, since each builder works a little differently and we don’t know which one you are going to choose. 🤷🏻♀️But If you want to learn more, don’t worry, usually the website and e-commerce builders provide detailed tutorials on how to use their individual theme and page builders. Here you can find some tutorials for the most common builders:
- Divi Builder Tutorial
- Elementor Academy
- Woocommerce Tutorials
- Wix Tutorials
- Shopify Tutorials
- Webflow Tutorials
- Squarespace Tutorials
And this one goes without saying, but once you determine your design and layout of your pages you will of-course have to fill them with your content, like video, text copies, image material and so on.
Step D
Website Set-up and Plugins

When you are done creating and designing your website there are some more basic things you should complete before your site goes life:
- Install a cookie banner
- Get your legal texts together
- Set up Google Analytics
- Submit your sitemap to Google Search Console
- Install any other necessary plugins
Let’s dive into each of those points individually:
Install a Cookie Banner:
Since the introduction of new Consumer Data Protection regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the CCPA in the US, using cookies on our website and collecting data from your users has become a little more complicated. You need to make sure to take all the measures to comply with the new regulations. These regulations vary depending on the country or region your users are located. For example, all websites and online services that process personal data of users located in the European Union, regardless of where the website owner is located, need to comply with the European GDPR, which are probably the most strict data protection regulations.
The GDPR requires website owners to obtain explicit consent from users for the use of cookies that collect personal data. This means that website owners must inform users about the types of cookies used, their purpose, and obtain their consent before the cookies are stored on the user’s device.
To comply with the GDPR, as a website owner you must provide a clear and prominent cookie banner or pop-up that informs users about the use of cookies and provides options for users to consent or refuse. The banner or pop-up should include a link to your website’s privacy policy that explains in detail how the cookies are used and how personal data is collected and processed. You also must provide users with a way to manage their cookie preferences, such as a consent manager. The consent manager should allow users to easily withdraw their consent or change their preferences at any time.
Therefore if you expect to have users located in Europe visiting your site, the best is to play save and use a so-called Cookie Management Platforms (CMP). A CMP is a tool that allows you as a website owner to obtain, manage, and document user consent for the use of cookies and other tracking technologies.
There are a number of CMP plugins or apps, some of them are even free to use. You will find a list of CMP plugins on your Website Creation Stack 📋List.
Get your legal texts together:
Furthermore, to ensure legal compliance of your website there are certain types of texts that you should not forget about. Again the requirements for legal compliance of a website may vary depending on the country or region where the website is based, the location of its users, and the nature of the website’s activities.
However, in general, there are three important documents that you should not forget about when setting up your site or online shop: the privacy policy, the terms & conditions and the imprint.
- Privacy policy: A privacy policy is generally required in most countries or regions if your website collects or processes personal data of users. This includes information such as names, email addresses, and other identifiable information. A privacy policy should outline how personal data is collected, used, and protected, as well as the user’s rights to access, correct, or delete their personal data. GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in the European Union and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) in California, USA, are some examples of laws that mandate the inclusion of a privacy policy.
- Terms & Conditions: Terms & conditions, also known as terms of service or terms of use, are typically required for websites that offer services, products, or content to users. They outline the rules and guidelines for using the website and its services, including the user’s rights and responsibilities, intellectual property rights, and limitations of liability. Terms & conditions are not mandatory in all countries, but they can help to protect the website owner’s interests and provide clarity to users on the terms of their use of the website.
- Imprint: An imprint is typically required in Germany, Austria, and Switzerland. If your website targets users in these countries, you may need to include an imprint that provides the legal and contact information of the website owner. An imprint may also be required in other countries or regions, so it’s important to check the specific requirements for your website’s target audience.
There are a number of online tools and plugins that you can use to automatically generate your privacy policy, terms & condition and imprint if needed. You will also find some on your Website Creation Stack 📋List.
However, here you will have to make sure you are using a tool that guarantees legal compliance with the regulations that apply for your website.
If you want to be on the really safe side, the best way is to consult with a lawyer to help you draft the legal documents you need.
Set up Google Analytics:
Of course, you also want to be able to analyze your website data. The probably most popular website analytics tool is Google Analytics.
Google Analytics is a free web analytics service provided by Google that tracks and reports website traffic and user behavior. It helps website owners and marketers to understand how visitors interact with their website, what content is popular, where visitors are coming from, and how long they stay on the site, among other things.
With Google Analytics, you can track various metrics such as:
- Audience data: demographic information such as age, gender, location, and interests of website visitors.
- Acquisition data: the channels through which visitors came to your website, such as organic search, paid search, social media, or referrals.
- Behavior data: the pages visited, the time spent on each page, and the actions taken on the website, such as clicks, downloads, and form submissions.
- Conversion data: the number of goals or conversions achieved on the website, such as newsletter signups, purchases, or leads generated.
Google Analytics works by placing a tracking code on your website that collects data and sends it back to Google servers. You can then access this data through the Google Analytics dashboard, which provides detailed reports and insights into your website’s performance. It is a powerful tool that can help you optimize your website, improve user experience, and increase conversions.
Google Analytics 4 (GA4) is the latest version of Google Analytics that was launched in October 2020. Google Analytics 4 uses machine learning to provide more accurate insights into user behavior and includes features like cross-device tracking, event-based tracking, and enhanced data privacy controls.
If you decide to use Google Analytics, make sure you let your website users know that you are doing so within your privacy policy and don’t forget to include the GA cookies in your CMP.
Here is how you set up Google Analytics for your website:
- Create a Google Analytics account: Go to the Google Analytics website and click on the “Start for free” button. Sign in with your Google account, or create a new one if you don’t have one.
- Set up a new property: Click on the “Admin” button in the bottom left corner and then select “Create Property” from the dropdown menu. Follow the instructions to provide information about your website, including the website name, URL, and time zone.
- Add the tracking code to your website: Once you have created a new property, you will be provided with a tracking code that you need to add to your website. Copy the tracking code and paste it into the header section of your website code, just before the closing </head> tag.
To find your tracking code and the instructions on how to Install the Google tag go to: Admin → Data Streams → click on your website name → scroll down and click on “View tag instructions”. Now you can choose between installing it manually or with a website builder/CMS
- Verify that your tracking code is working: After adding the tracking code, you can verify that it is working correctly by going to the “Real-Time” section in Google Analytics and checking if your website is listed as an active user.
- Set up goals: Goals are specific actions that you want visitors to take on your website, such as filling out a contact form or making a purchase. To set up goals, go to the “Admin” section, select the property you want to add goals for, and click on “Goals.” Follow the instructions to set up your goals.
- Configure filters and views: Filters allow you to exclude or include specific data from your reports, while views are different ways of looking at your data. To set up filters and views, go to the “Admin” section, select the property you want to configure, and click on “Filters” or “Views.” Follow the instructions to set up filters and views that are relevant to your website.
- Set up E-commerce tracking: If you have an e-commerce website, you can set up e-commerce tracking to track your website’s transactions and revenue. To set up e-commerce tracking, go to the “Admin” section, select the property you want to configure, and click on “E-commerce Settings.” Follow the instructions to set up e-commerce tracking for your website.
Submit your Sitemap to Google Search Console:
In order for your website to be found on the Google Search Results, when users search for certain terms, Google needs to index your site first. Indexing a website means that search engines like Google have crawled your website and added it to their database of web pages. When a website is indexed, it means that its pages are now eligible to appear in search results when users search for relevant terms or phrases.
When a search engine crawls a website, it sends out automated bots called “spiders” to follow links on the pages of the website and analyze the content of those pages. The search engine then adds the information it collects to its index, which is essentially a huge database of all the web pages it has crawled.
Once a website is indexed, it can start appearing in search results for relevant queries.
Google has a massive web crawler called Googlebot that continuously crawls the web, discovering and indexing new pages. However, it is not guaranteed that Google will automatically index your new website or its pages right away.
In general, new websites and pages will eventually be discovered and indexed by Google, but the speed at which this happens can vary depending on several factors, such as the quality of your content, the structure of your website, the number and quality of backlinks pointing to your site, and the frequency of updates to your site.
To help speed up the process of getting your new site indexed, you can apply Search Engine Optimization best practices. (we will take a detailed look into SEO in a moment) and submit your sitemap to Google Search Console:
- Create a sitemap: A sitemap is a file that lists all the pages on your website. It helps search engines like Google understand the structure of your website and find all your pages. You can use a sitemap generator tool, to create your sitemap. You will find a number of tools on your Website Creation Stack 📋List.
- Submit your sitemap to Google Search Console: Google Search Console is a free tool provided by Google that allows website owners to monitor and optimize their site’s presence in Google search results. You can submit your sitemap to Google Search Console to help Google find and index your pages more quickly.
Install any other Necessary Plugins:
Finally you also want to make sure to install any additional plugins or apps you need. Plugins are software components that can be added to an existing program or application like your wordpress CMS or other website builders like Wix, Shopify or Squarespace, to extend its functionality. They are designed to provide additional features or capabilities that are not included in the original software. Plugins are typically created by third-party developers and are made available to users as separate downloads or add-ons.
Plugins are often designed to be modular and can be easily installed and removed without affecting the underlying software. This makes it easy for users to customize their software to meet their specific needs and preferences.
Common types of plugins include for example:
|
Plugin Category |
Description |
|
SEO Plugins |
Helps improve website search engine rankings by optimizing website content, metadata, and sitemaps. |
|
E-commerce Plugins |
Adds e-commerce functionality to a website, including product listings, shopping carts, payment gateways, and order management. |
|
Social Media Plugins |
Helps integrate social media functionality into a website, including sharing buttons, social media feeds, and social media login. |
|
Security Plugins |
Helps improve website security by providing features such as malware scanning, firewalls, and login protection. |
|
Contact Form Plugins |
Helps add contact forms to a website to allow visitors to send messages to the website owner or business. |
|
Analytics Plugins |
Helps track and analyze website traffic and user behavior, including page views, bounce rates, and click-through rates. |
|
Backup and Restore Plugins |
Helps create backups of a website and restore it in case of data loss or website crashes. |
|
Performance Optimization Plugins |
Helps improve website speed and performance, including caching plugins and image optimization plugins. |
|
Membership Management Plugins |
Helps manage user access to specific content on a website by creating membership plans, restricting access to certain pages or content, and managing user accounts and subscriptions. |
💡You will find a selection of useful website plugins on the List above.
Please note that neither the plugin categories nor the plugin list is 100% exhaustive. There are thousands of plugins in a lot of different categories. You will need to define which type of functionalities you want to add to your page and there plugins will be necessary. When you research plugins the number of downloads and ratings give you a good orientation about the quality of the individual plugin.
Step E
SEO Optimization

Finally you want to work on your Search Engine Optimization (SEO), meaning you want to optimize your website to improve its visibility and ranking in search engine results pages (SERPs). The goal of SEO is to increase the organic (non-paid) traffic to your website by improving your website’s search engine rankings for specific keywords or phrases.
Effective SEO requires you to gain an understanding of search engine algorithms and your user behavior. Which is why you will have to ongoingly test and analyze your SEO activities to refine and optimize your strategy over time.
💡 You will find a selection of SEO tools on the List above.
You can differentiate between three large categories of SEO techniques, that include a number of activities that you can conduct to impact your website ranking:
On-page optimization:
- Conduct keyword research to identify relevant, high-traffic keywords for your content
- Use your target keyword in the page title, URL, and meta description
- Optimize headings (H1, H2, etc.) with relevant keywords
- Provide (blog) content that is high-quality, original, and provides value to users
- Optimize images with descriptive file names and alt tags
- Include internal links to other relevant content on your website
- Use schema markup to provide search engines with additional information about your content
Off-page optimization:
- Build high-quality, relevant backlinks from other websites to your content
- Leverage social media to promote your content and engage with your audience
- Participate in online forums and communities related to your industry or niche
- Guest post on other relevant websites to expand your reach and build authority
- Monitor your online reputation and address any negative reviews or comments promptly
Technical optimization:
- Ensure your website is mobile-friendly and loads quickly on all devices
- Use HTTPS encryption to ensure data security and improve search engine rankings
- Implement structured data to help search engines better understand your content
- Optimize site architecture and navigation to improve user experience and search engine crawling
- Regularly audit and update your website to ensure it is free of broken links and other technical issues.
There are a number of SEO plugins that help you optimize your on-page SEO, you will find various of them on your SEO Stack 📋List.
Keyword Research
As mentioned above, one of the first steps is to research your keywords, meaning you want to identify and analyze the keywords and phrases that people use to search online for information, products, or services that your business provides or that are related to it. It is a critical component of any SEO or content marketing strategy because it helps website owners and marketers understand what their target audience is searching for and how to create content that addresses their needs.
There are a number of tools like ahrefs, moz or semrush that can help you identify popular and relevant keywords related to your business, products, or services and analyze their search volume, competition and relevance to determine which ones are most important and should be prioritized. You will find a number of example tools on your SEO Stack 📋List.
SEO Performance Analysis
Those same tools also help you to understand your search engine performance as well as the one of your competitors. Plus they can help you understand your competitors’ SEO strategies by analyzing their keyword rankings, backlinks, traffic and other metrics.
The different tools use different, sometimes proprietary, types of KPIs to evaluate a website’s search engine performance, examples are:
- Domain Authority (DA): a metric developed by Moz that measures the overall strength and authority of a website’s domain. It is calculated based on a variety of factors, including the number and quality of backlinks pointing to the site, the age of the domain, and other factors.
- Page Authority (PA): another metric developed by Moz that measures the strength and authority of a specific page on a website. It is calculated based on factors such as the number and quality of backlinks pointing to the page, the content on the page, and other factors.
- Domain Rating (DR): a metric developed by Ahrefs that measures the backlink profile of a website. It ranges from 0 to 100 and is based on the quantity and quality of backlinks pointing to a website, as well as other factors such as the diversity of the backlink profile and the freshness of the links.
- Referring Domains: a metric that shows the number of unique domains that are linking to a website. A higher number of referring domains generally indicates a stronger and more diverse backlink profile, which can positively impact a website’s search engine rankings.
- Backlinks or Backlink Profile: a metric that measures the number and quality of backlinks pointing to a website or specific page. Backlinks are a key factor in SEO, as they signal to search engines that other websites consider your content to be valuable and relevant.
- Organic Traffic: a metric that measures the amount of traffic a website receives from organic search results. Organic traffic is an important indicator of SEO performance, as it shows how well a website is ranking for relevant keywords and attracting visitors from search engines.
- Organic Keywords: a metric that shows the number of keywords a website is ranking for in organic search results. A higher number of organic keywords generally indicates better SEO performance and a stronger overall online presence.
- Keyword Rankings: a metric that shows where a website or specific page ranks in search engine results pages (SERPs) for specific keywords or phrases. Higher rankings generally indicate better SEO performance.
- Click-through Rate (CTR): a metric that measures the percentage of people who click on a link to a website after seeing it in search engine results pages (SERPs). A higher CTR generally indicates better SEO performance, as it shows that a website’s title and meta description are compelling and relevant to searchers
With this we have covered the most important points for creating your website or online shop. As you see there are a lot of tools out there that enable even non-tech founders, who are willing to learn and dedicate some time, to set up their online presence.